- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Particle Size:
-
40-75μm
-
Mechanism:
-
SCX/SAX/C18/C8/C4/NH2/HLB
-
Application:
-
Lab Research
-
Certificate:
-
CE ISO
-
MOQ:
-
1 Pcs
-
OEM:
-
Avalibale
-
Housing Material:
-
PP
-
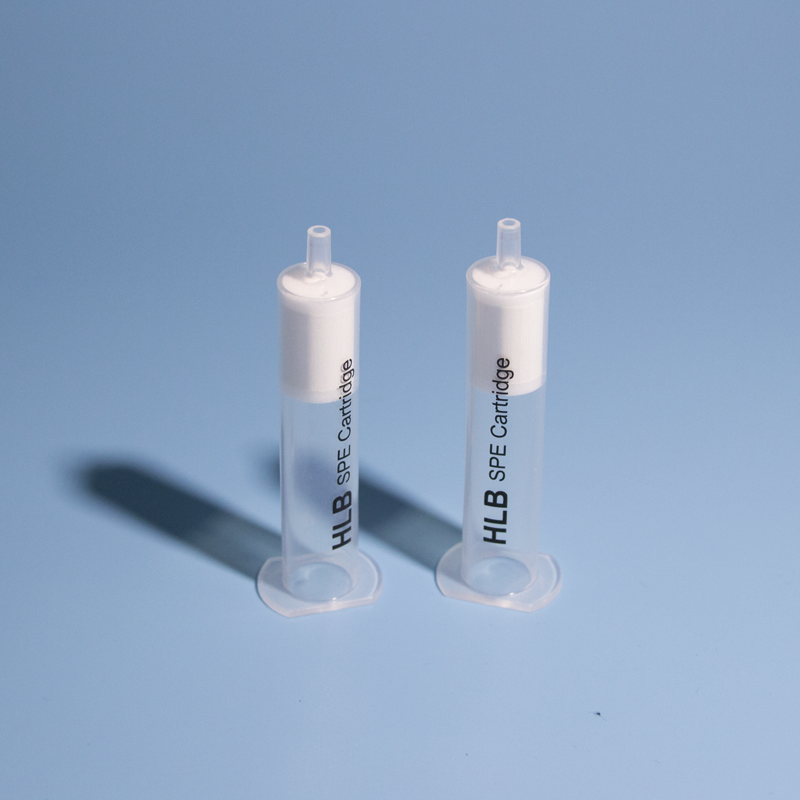
Product name:
-
SPE Column
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
Shaanxi, China
-
Pore Size:
-
60/70/120A
-
Volume:
-
1/2/6/12mL
-
Particle Size:
-
40-75μm
-
Mechanism:
-
SCX/SAX/C18/C8/C4/NH2/HLB
-
Application:
-
Lab Research
-
Certificate:
-
CE ISO
-
MOQ:
-
1 Pcs
-
OEM:
-
Avalibale
-
Housing Material:
-
PP
-
Product name:
-
SPE Column
Description
Hawach SPE Cartridges are made of medical grade PP and forming in one time. Frits are made of UHMW-PE. There is a variety of models to choose. Hawach provides SPE OEM service in order to support you to establish your own SPE brands easily.

Selection
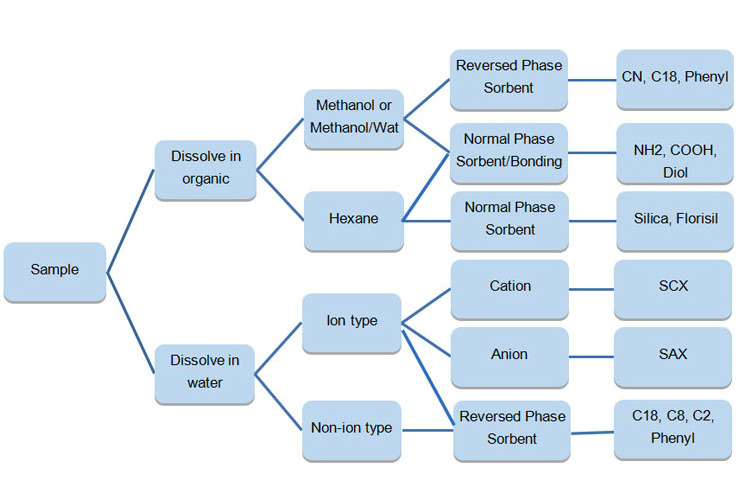
Select proper sorbent according to the difference between target analytes and disruptors such as polar, molecular weight and pKa, etc.
For reverse phase, normal phase and adsorption type SPE cartridges, the quantity of target analytes to SPE sorbent ratio is generally not more than 5%. For ion exchange SPE cartridges, need to consider the ion exchange capacity. Provide the conventional ion exchange capacity of Hawach is about 0.3meq/g, the following table for SPE cartridges capacity parameters
|
Specification |
Maximum Sample Load |
Volume |
Minimum Elution volume |
|
50-100mg |
2.5mg-5mg |
1mL |
100-200μL |
|
100-200mg |
5mg-10mg |
3mL |
200-500μL |
|
200mg-1g |
10mg-50mg |
6mL |
500μL-6mL |
|
500mg-2g |
25mg-100mg |
12mL |
3mL-10mL |
Operation Steps
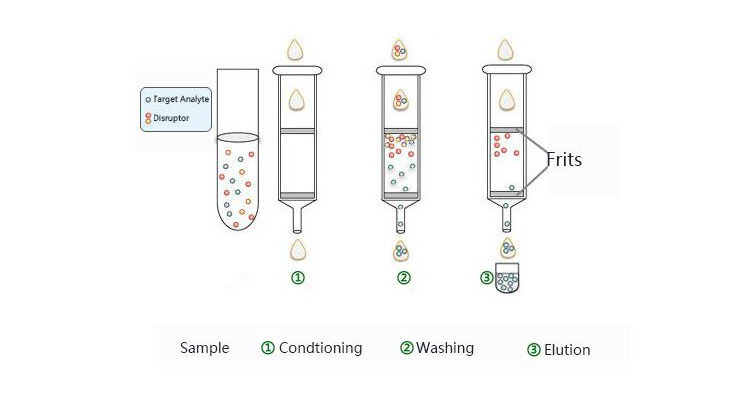
According to the different sorbent retention mechanism (sorbent retain target analytes or retain impurities), the operation is slightly different.
1. Sorbent
R
etain
T
arget
A
nalytes
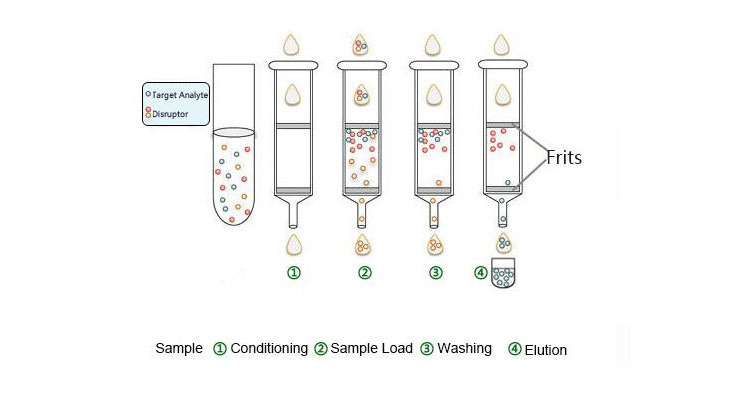
SPE operations are generally four step
s:
(1) Conditioning and equilibration:
Solvent is passed through the SPE material to wet the bonded functional groups => ensures consistent interaction.Sorbent/ phase is treated with a solution that is similar (in polarity, pH, etc.) to the sample matrix => maximizes retention.
(2) Sample Load:
Introduction of the sample = analytes of interest are bound/ extracted onto the phase/sorbent.
(3) Washing:
Selectively remove unwanted interference co-extracted with the analyte without prematurely eluting analytes of interest.
(4) Elution:
Removing analytes of interest with a solvent that overcomes the primary and secondary retention interactions between sorbent and analytes of interest.
2. Sorbent Retain Disruptors
SPE operations are generally three steps:
(1) Conditioning and equilibration:
Solvent is passed through the SPE material to wet the bonded functional groups => ensures consistent interaction.Sorbent/ phase is treated with a solution that is similar (in polarity, pH, etc.) to the sample matrix => maximizes retention.
(2) Sample Load:
disruptors are bound/ extracted onto the phase/sorbent. Target analytes pass through cartridge with solution. Should collect solution in this step.
(3) Elution:
Removing analytes of interest with a solvent that overcomes the primary and secondary retention interactions between sorbent and analytes of interest. Combine the solution with step (2).