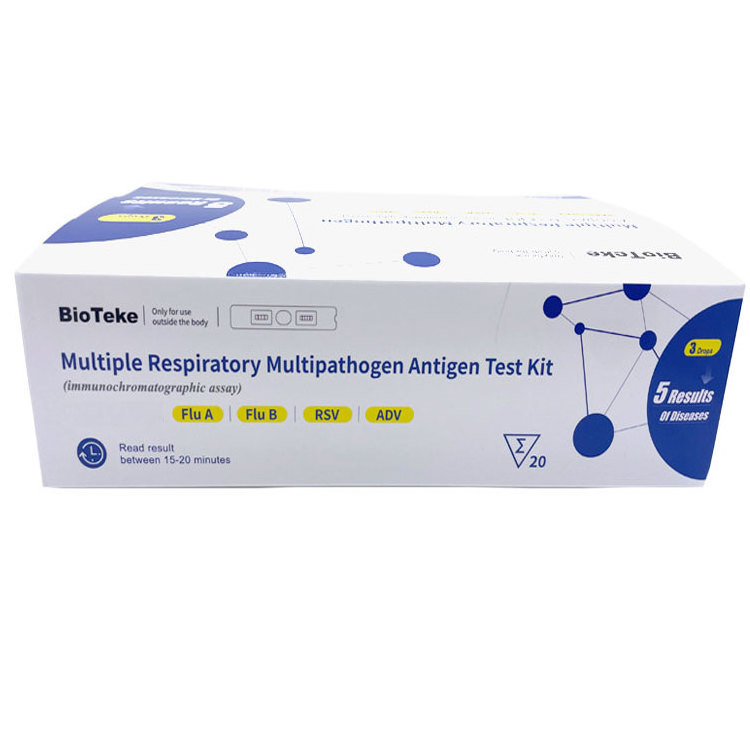
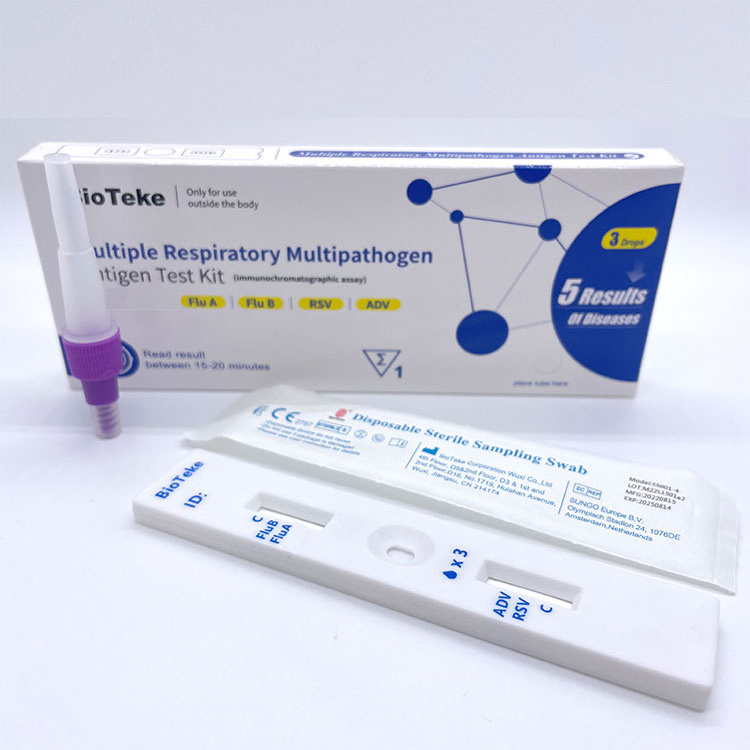
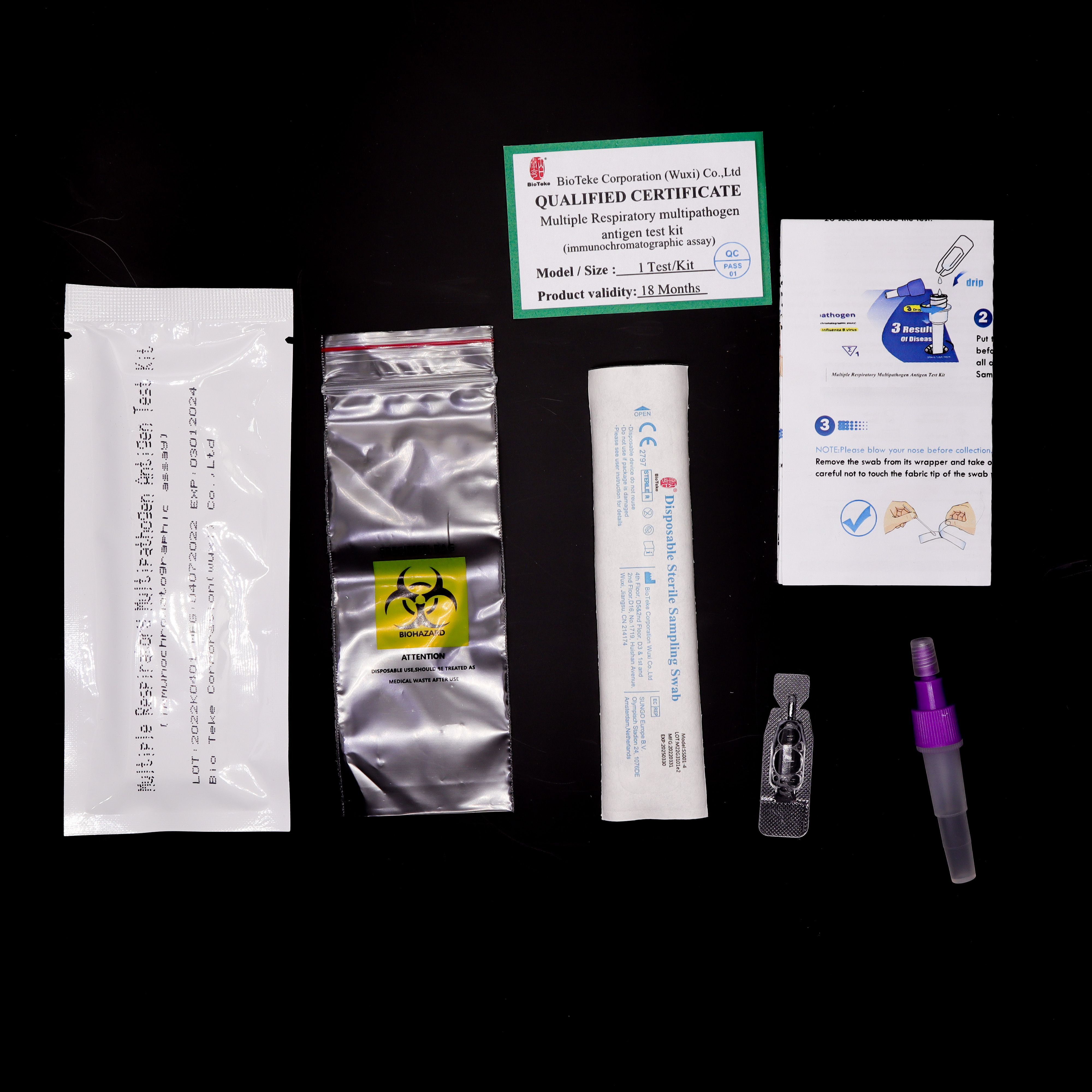
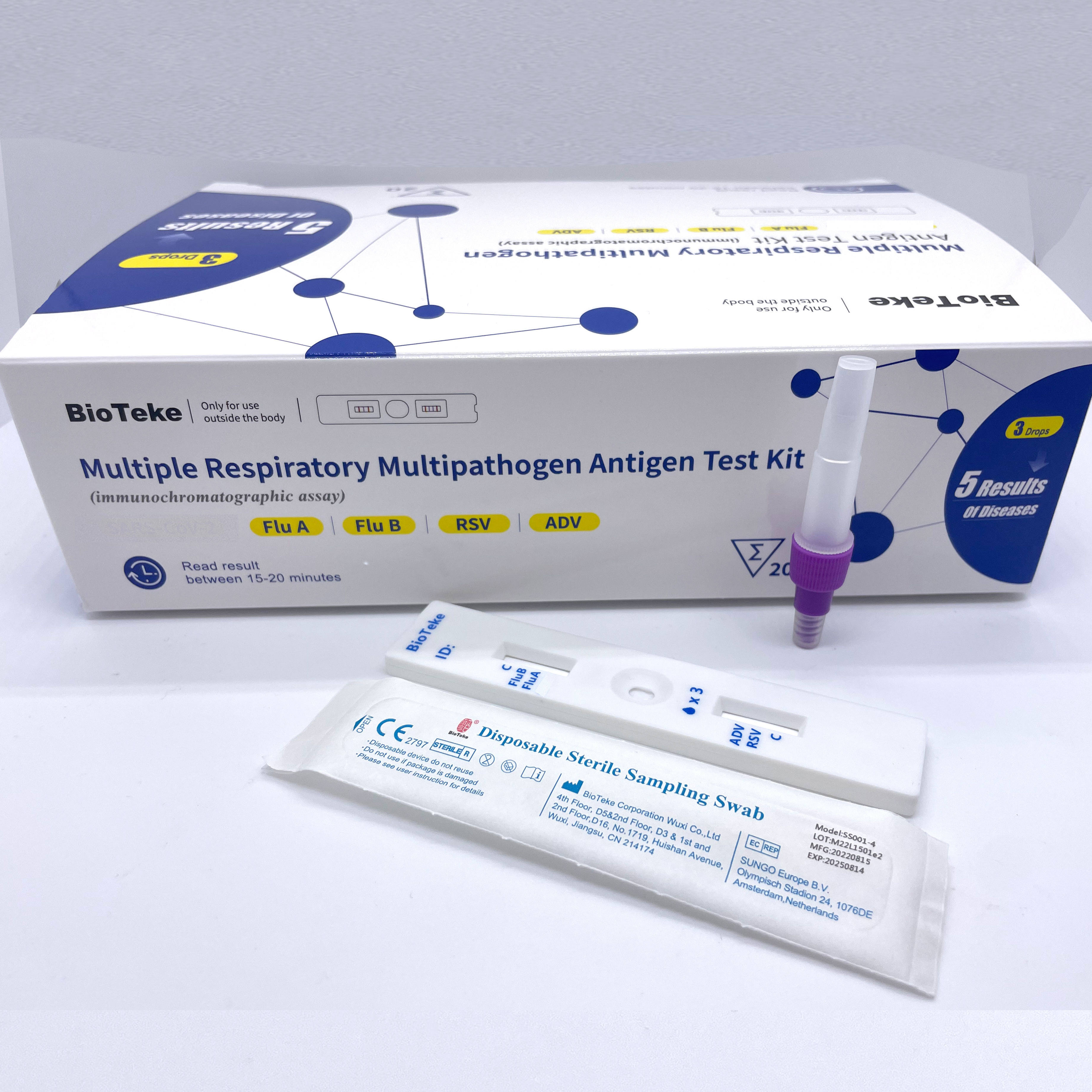
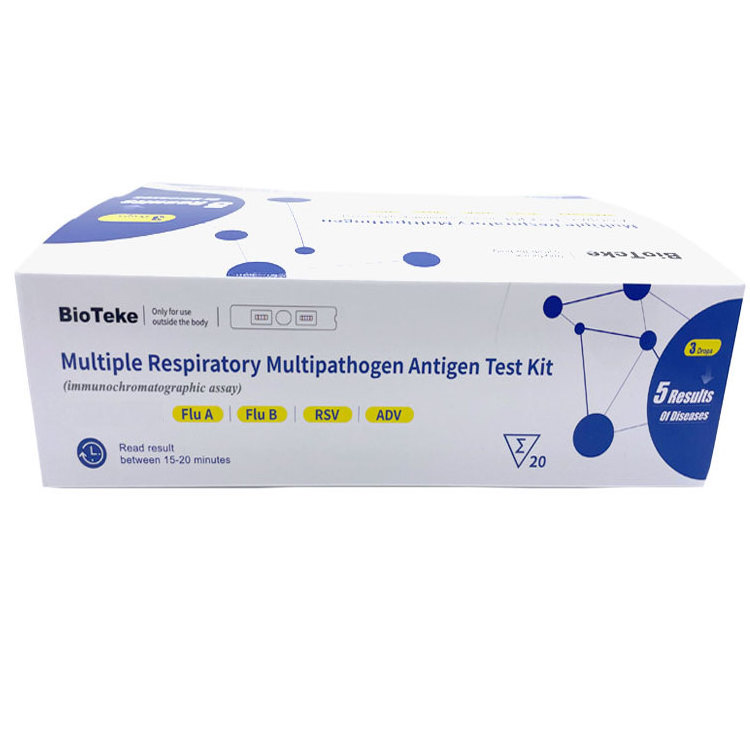
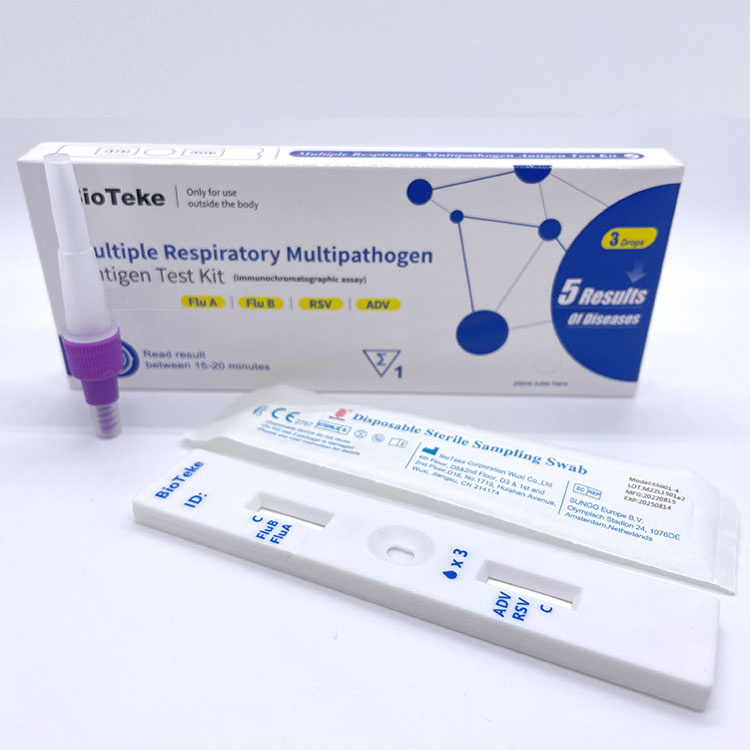
Immunochromatography
is a simple and rapid diagnostic method commonly used for the detection of influenza antigens.
The basic principle is as follows:
The patient's throat swab sample is loaded onto the sample pad on the test card. The influenza virus antigens in the sample will bind to the labeled detection antibodies. The mixture passes through the capture antibody area, which is fixed to a specific area on the membrane and specifically binds to the influenza virus antigen. If there is influenza virus antigen in the sample, the labeled antibody-antigen complex will form a visual signal in the capture antibody area.