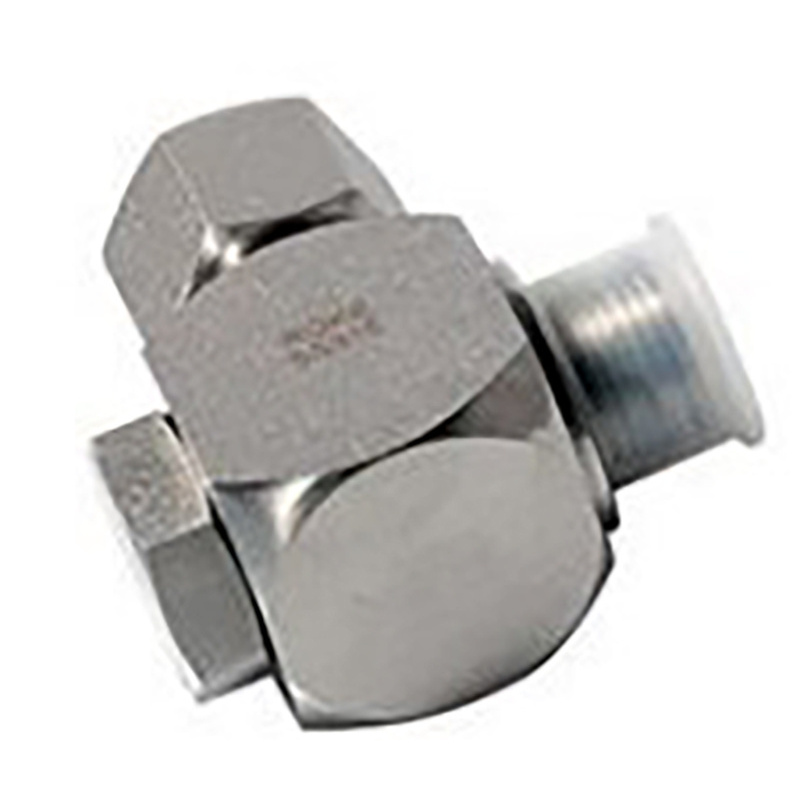
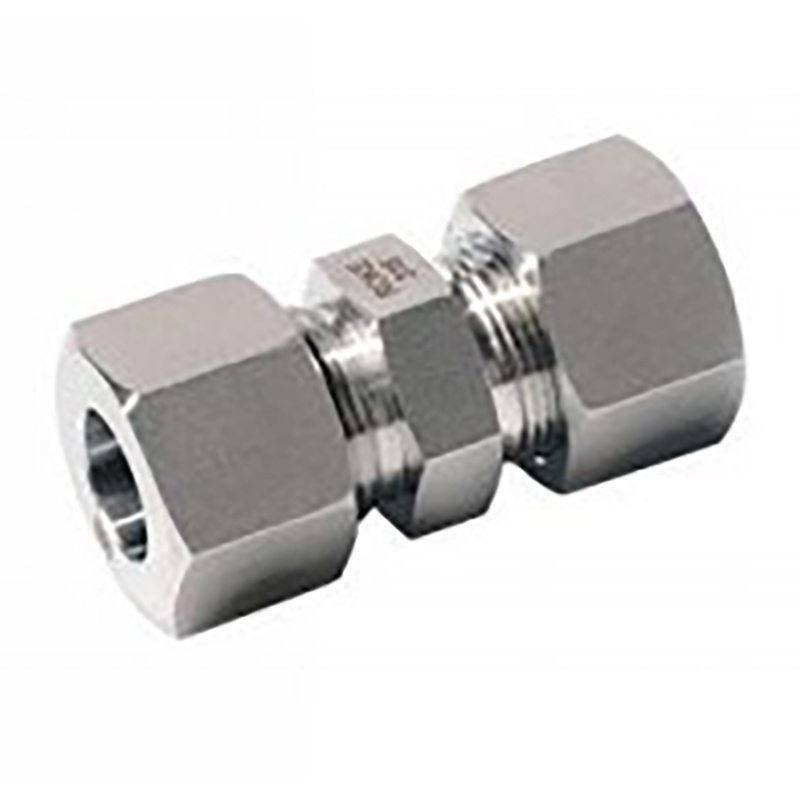
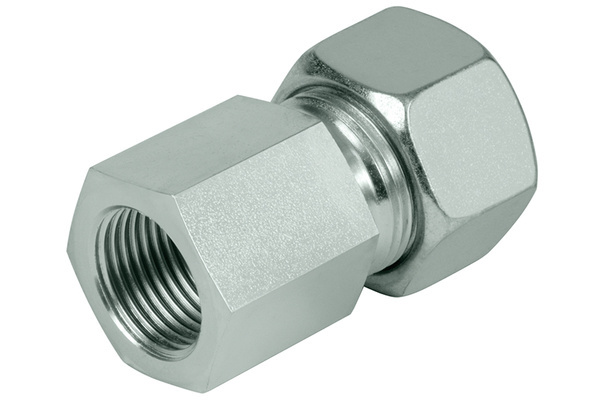
2. Lightly remove chips and particles from the inside and outside cut edges of tube. Bevel up to 0.2mm × 45 is permissible.
3. For tube bend, the minimum height from the straight pipe end to the bending radius must be at least twice the
height of the nut.
4. Lubricate thread and cone of the fitting body, ring and thread of nut.
- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Weight:
-
10
-
Bore diameter:
-
60-100
-
Rod diameter:
-
25-45
-
Stroke:
-
32-1500
-
Installation distance:
-
109-1808
-
working pressure:
-
18Mpa
-
Interface dimensions:
-
2-M14*1.5
-
weight:
-
3.4kg-46kg
Quick Details
-
Warranty:
-
1 Year
-
Brand Name:
-
ever-power
-
Place of Origin:
-
Zhejiang, China
-
Weight:
-
10
-
Bore diameter:
-
60-100
-
Rod diameter:
-
25-45
-
Stroke:
-
32-1500
-
Installation distance:
-
109-1808
-
working pressure:
-
18Mpa
-
Interface dimensions:
-
2-M14*1.5
-
weight:
-
3.4kg-46kg

Product Description
High Pressure: This indicates that the fitting is designed to handle hydraulic systems operating at high pressure levels. High-pressure fittings are typically constructed with materials and designs that can withstand the elevated pressures without leaking or failing.
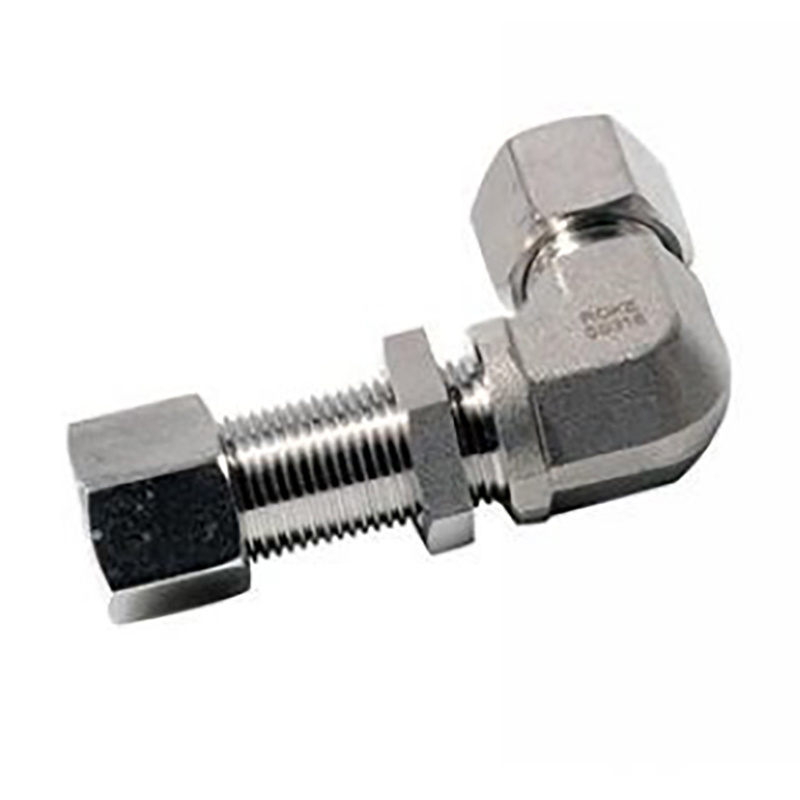
Banjo: A banjo fitting is a type of hydraulic fitting that typically consists of a hollow bolt with a hole through the side. The fitting is named after its resemblance to a banjo musical instrument. Banjo fittings are commonly used in applications where fluid flow needs to be directed at a right angle to the fitting.
Elbow: An elbow fitting has a curved or angled shape, allowing the hydraulic lines or hoses to make a directional change. In this case, the banjo fitting has an elbow shape, indicating that it is designed to direct fluid flow at a specific angle or orientation.
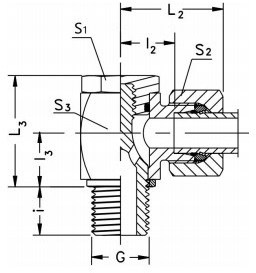
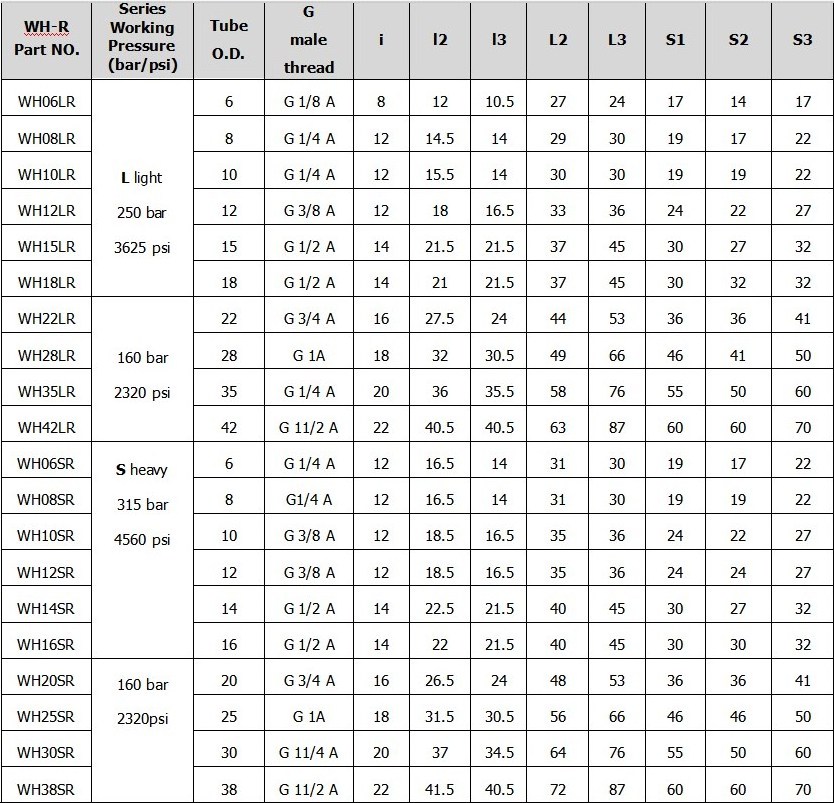
WH-R: The specific meaning of "WH-R" is not immediately clear without additional context. It could be a part number, manufacturer's code, or a specific designation related to the fitting's size, thread type, or other characteristics. Without further information, it's challenging to provide a precise interpretation of this specific code.
Application of Elbow-WH-R hydraulic fittings
1.Routing Hydraulic Lines: Elbow fittings are used to route hydraulic lines around obstacles or tight spaces, allowing for efficient installation and proper alignment of hydraulic hoses or pipes.
2.Hydraulic Systems in Machinery: Elbow fittings are commonly used in various machinery and equipment that utilize hydraulic systems, such as construction machinery, agricultural equipment, industrial machinery, and more.
3.Piping Systems: Hydraulic elbow fittings can be used in hydraulic piping systems to change the direction of fluid flow, ensuring proper fluid circulation and efficient operation.
4.Hydraulic Power Units: Elbow fittings are used in hydraulic power units to connect hydraulic hoses or pipes, allowing for the transfer of hydraulic fluid between different components, such as pumps, valves, cylinders, and motors.
It's important to note that the specific application of hydraulic fittings, including elbow fittings, can vary depending on the system requirements, equipment design, and hydraulic system specifications. It is always recommended to consult the manufacturer's guidelines or seek assistance from a hydraulic expert to ensure the proper selection and application of hydraulic fittings for a specific system.

Installation instructions
The nuts of ROKE hydraulic connectors are all silver plated and coated with our patented nano lubricating layer. Through this method, the installation torque can be controlled within a reasonable range.
Especially in narrow spaces or suspended operations, installation is very easy.
In order to assemble correctly, the assembly instructions should be followed. Improper assembly may cause malfunctions or damage safety.
1. Cut the tube: 1/2 angle tolerance to the tube axis is permissible. Tube cutter is not recommendable.
Assembly
5. Slip nut and then ring onto the tube end. Ensure that the ring is placed correctly.
6. Screw nut manually onto fitting body until finger tight. Hold the tube against the shoulder in the cone of the fitting body.
7. Mark nut and tube for measuring the prescribed turns of the nut.
8. Tighten the nut 1 1/4 turns. Tube must not turn with tube. Stop edge of the ring limits over-tightening by increasing tightening torque.
5. Slip nut and then ring onto the tube end. Ensure that the ring is placed correctly.
6. Screw nut manually onto fitting body until finger tight. Hold the tube against the shoulder in the cone of the fitting body.
7. Mark nut and tube for measuring the prescribed turns of the nut.
8. Tighten the nut 1 1/4 turns. Tube must not turn with tube. Stop edge of the ring limits over-tightening by increasing tightening torque.
Check & Final Assembly
9. Loosen nut and remove ring-mounted tube from fitting. And check if a visivle collar has formed on the pipe in
front of the first cutting edge. If not, tighten slightly more.
10. Insert the pre-assembled tube into the fitting.
While holding fitting body with a wrench, tighten nut approx. 1/4 revolution beyond the point of a clearly perceptible resistance.
9. Loosen nut and remove ring-mounted tube from fitting. And check if a visivle collar has formed on the pipe in
front of the first cutting edge. If not, tighten slightly more.
10. Insert the pre-assembled tube into the fitting.
While holding fitting body with a wrench, tighten nut approx. 1/4 revolution beyond the point of a clearly perceptible resistance.
Hot Searches