- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
MF:
-
SiO2
-
Place of Origin:
-
Hebei, China
-
Appearance:
-
White or light yellow powder, powder
-
Application:
-
Industrial, Medical
-
Brand Name:
-
yingye
-
Model Number:
-
G
-
Product name:
-
Silicon dioxide
-
Color:
-
Yellow or white
-
FOB:
-
TIANJIN,XINGANG PORT ,CHINA
-
Packing:
-
25kg/bag, 50kg/bag
-
Sample:
-
Free(500g)
-
MOQ:
-
10MT
-
Usage:
-
Coatings, Pharmaceuticals
Quick Details
-
CAS No.:
-
14808-60-7
-
Purity:
-
99%, 99%min,
-
Other Names:
-
Silicon dioxide
-
MF:
-
SiO2
-
Place of Origin:
-
Hebei, China
-
Appearance:
-
White or light yellow powder, powder
-
Application:
-
Industrial, Medical
-
Brand Name:
-
yingye
-
Model Number:
-
G
-
Product name:
-
Silicon dioxide
-
Color:
-
Yellow or white
-
FOB:
-
TIANJIN,XINGANG PORT ,CHINA
-
Packing:
-
25kg/bag, 50kg/bag
-
Sample:
-
Free(500g)
-
MOQ:
-
10MT
-
Usage:
-
Coatings, Pharmaceuticals
Product introduction

Silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SiO2. Silicon atoms and oxygen atoms are arranged in a long-range order to form crystalline silicon dioxide, and short-range order or long-range disordered arrangement to form amorphous silicon dioxide.
In a silicon dioxide crystal, the silicon atom is located in the center of the regular tetrahedron, and the four oxygen atoms are located on the four top angles of the regular tetrahedron, and many such tetrahedrons are connected by the oxygen atoms of the top angles, each oxygen atom is shared by the two tetrahedrons, that is, each oxygen atom is combined with two silicon atoms.
The simplest form of silicon dioxide is SiO2, but it does not represent a simple molecule (only the ratio of the number of atoms of silicon and oxygen in the silicon dioxide crystal).
Pure natural silica crystal, is a hard, brittle, insoluble colorless transparent solid, often used in the manufacture of optical instruments.
Specification

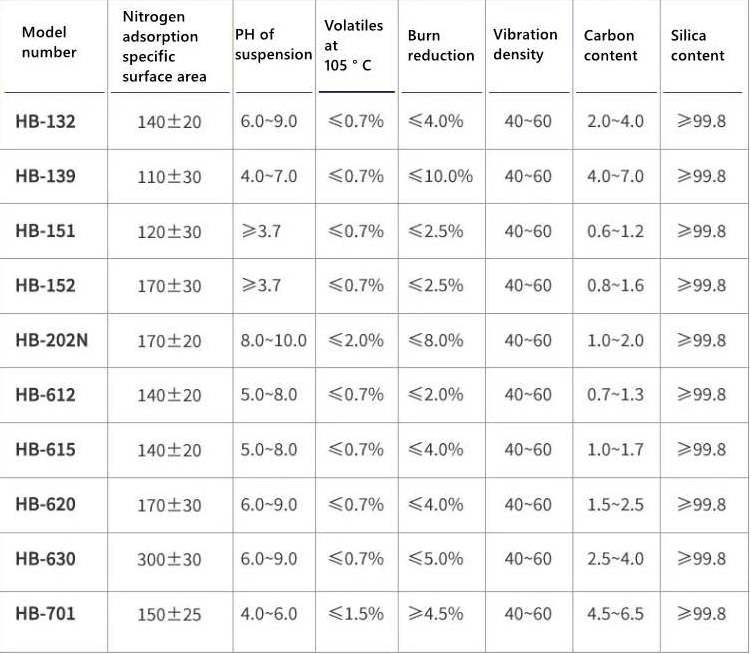
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product application

The chemical formula of silicon dioxide is SiO2, which has two forms: crystalline and amorphous. [2]
Silica existing in nature, such as quartz, quartz sand, etc. are collectively referred to as silica. [2]
Pure quartz is colorless crystal, large and transparent prismatic quartz crystal is called crystal, containing trace impurities and purple is called amethyst, light yellow, golden and brown smoke crystal. [2]
Chalcedony, agate, and jasper are colored quartz crystals that contain impurities. Sand is fine grains of quartz mixed with impurities. Opal and diatomite are amorphous silica. [2]
Silica has a wide range of uses, mainly used in glass, water glass, pottery, enamel, refractory materials, aerogel felt, ferrosilicon, molding sand, elemental silicon, cement, etc. In ancient times, silica was also used to make porcelain glaze and carcass. [2]
The general stone is mainly composed of silica, calcium carbonate and other components. [2]
Crystalline silica has a melting point of 1723℃, a boiling point of 2230℃, and is insoluble in water. Except for fluorine gas and hydrofluoric acid, silica does not react with halogens, hydrogen halides and inorganic acids, but is soluble in hot concentrated bases, molten strong bases or sodium carbonate. [2]
In addition, silica can be reduced by coke and magnesium at high temperatures. At room temperature, the strong alkali solution and SiO2 will slowly react to produce silicate, so the glass bottle storing the strong alkali solution can not be ground glass stopper (glass containing SiO2), otherwise it will generate viscous sodium silicate Na2SiO3, so that the stopper and the bottle mouth bond together. Because SiO2 can react with hydrofluoric acid, glass containers cannot be used to contain hydrofluoric acid.
Hot Searches













