- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
Jiangsu, China
-
Brand Name:
-
BEST
-
Dimension(L*W*H):
-
As your requests
-
Weight:
-
0.5 KG
-
Working Temperature Range:
-
1 - 870 ℃
-
Material:
-
Stainless Steel, Incoloy
-
Core Components:
-
Heating wire
-
Tube Diameter:
-
8mm/10mm/12mm/14mm/16mm etc.
-
Application:
-
Oil, water ,other liquid etc
-
Max temperature:
-
870c(1600F)
-
Packaging:
-
Plastic bag, Carton box, Wooden box
-
Product name:
-
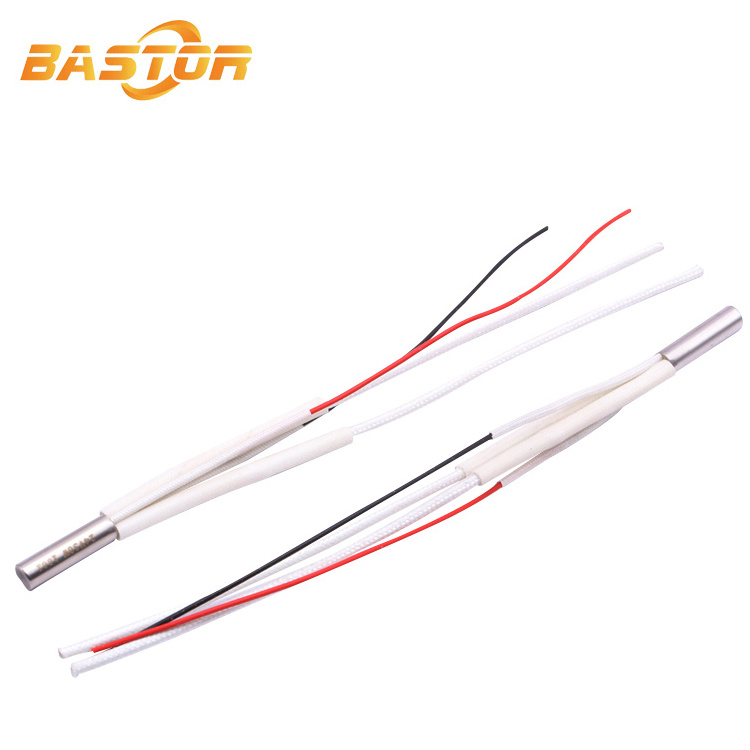
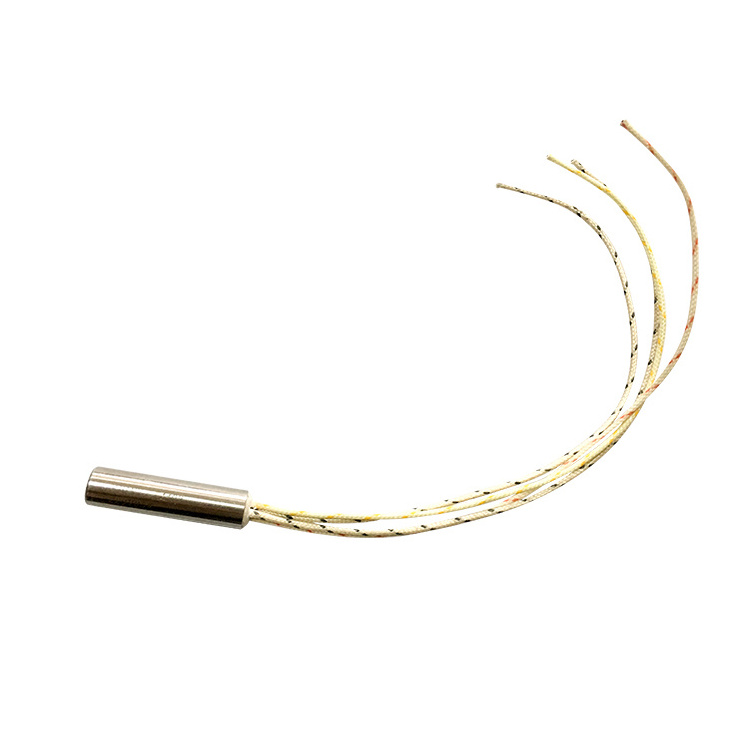
air heater element 500w 220v cartridge heater with k type thermocouple
-
After Warranty Service:
-
Video technical support
Quick Details
-
Type:
-
Air Heater
-
Power Source:
-
Electric
-
Voltage:
-
12-480V or customized
-
Place of Origin:
-
Jiangsu, China
-
Brand Name:
-
BEST
-
Dimension(L*W*H):
-
As your requests
-
Weight:
-
0.5 KG
-
Working Temperature Range:
-
1 - 870 ℃
-
Material:
-
Stainless Steel, Incoloy
-
Core Components:
-
Heating wire
-
Tube Diameter:
-
8mm/10mm/12mm/14mm/16mm etc.
-
Application:
-
Oil, water ,other liquid etc
-
Max temperature:
-
870c(1600F)
-
Packaging:
-
Plastic bag, Carton box, Wooden box
-
Product name:
-
air heater element 500w 220v cartridge heater with k type thermocouple
-
After Warranty Service:
-
Video technical support
Product Description
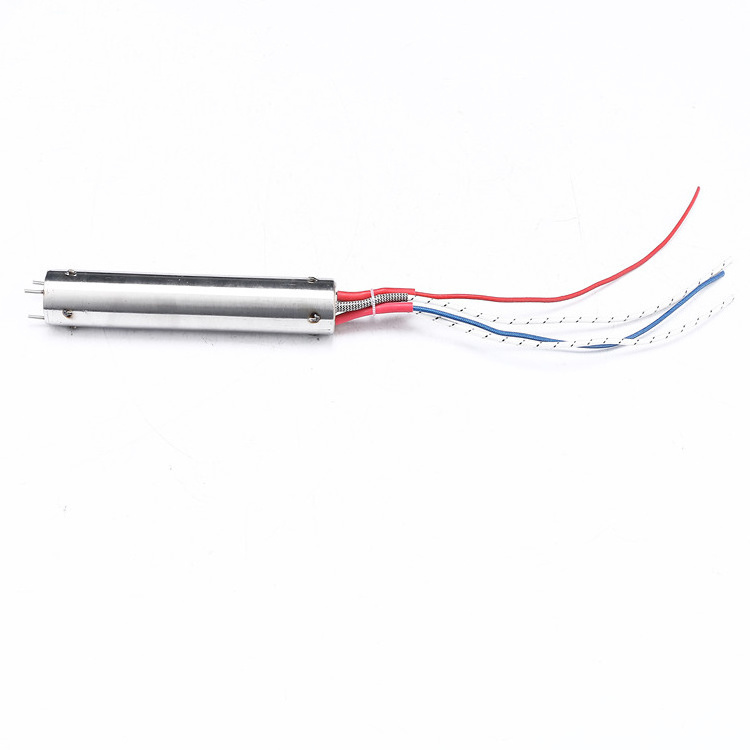
cartridge heater is an electric heating element that is typically cylindrical in shape and is used to provide
localized heat in industrial and commercial applications. It is made of a resistive heating element, such
as a Nichrome wire, that is embedded in a metal sheath.
When electric current is passed through the resistive heating element, it heats up and transfers heat to
the metal sheath. The metal sheath then conducts the heat to the surrounding environment, providing
localized heat in the area where the cartridge heater is installed.
Cartridge heaters are often used in applications such as plastic injection molding, hot stamping, and
packaging equipment, where precise and consistent heating is required. They can also be used in
laboratory and medical equipment, where precise temperature control is critical.
One advantage of cartridge heaters is their high heating capacity in a small size, which allows them to be
easily installed in tight spaces. They are also highly customizable, with a variety of options for size,
wattage, voltage, and other specifications.
| Resistance heating wire | NiCr 80/20 wire |
| Wattage Tolerance | +5%, -10% |
| Resistance tolerance | +10%, -5% |
| Length tolerance | ±1 mm |
| Diameter tolerance | ± 0.02mm |
| Standard Cold Zone | 5-10mm |
| Insulation resistance (cold) | ≥ 500 MΩ |
| Maximum leakage current (cold) | ≤ 0.5 mA |
| Thermocouple Location | type J / K / Ground wire |



Advantages
internal wiring: high temperature resistance, uniform heating, high thermal conductivity and difficult
cable fracture.
external wiring: high temperature resistance, uniform heating and high thermal conductivity.

The port part of the heating tube adopts terminal connection mode Is resistant to
high temperature and works in the heating medium which can not conduct wiring at both ends.
Cartridge heaters are a type of electric heating element that are commonly used in industrial settings to provide localized heating in machinery and equipment. Here are the basic steps involved in manufacturing cartridge heaters:
Core wire selection: The core wire is the heating element of the cartridge heater and is usually made of nickel-chromium or iron-chromium alloys. The wire is selected based on the required wattage and operating temperature of the cartridge heater.
Coil winding: The core wire is wound around a ceramic or metallic core to create the heating element. The number of turns and the diameter of the wire are determined based on the desired electrical resistance and watt density of the heater.
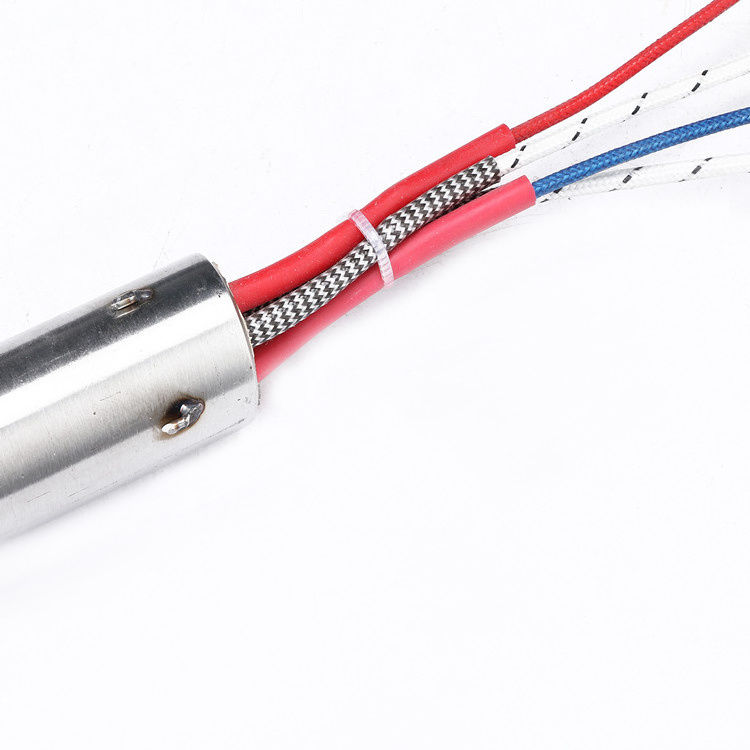
Core assembly: The heating element is inserted into a metal sheath, which is usually made of stainless steel or Incoloy. The ends of the core wire are welded or crimped to lead wires that will provide power to the heater.
Sealing and insulation: The ends of the metal sheath are sealed with ceramic or epoxy material to prevent moisture and contaminants from entering the heater. The entire assembly is then insulated with magnesium oxide powder to improve heat transfer and electrical insulation.
Finishing: The cartridge heater is cut to the required length and the lead wires are attached to terminal blocks or connectors. The heater may be coated with a protective layer to resist corrosion or abrasion.
Testing: The finished cartridge heater is tested to ensure that it meets the required specifications for electrical resistance, wattage, and insulation resistance.
Manufacturing cartridge heaters requires specialized equipment and expertise in electrical engineering and metalworking. It is important to follow safety procedures and quality control measures to ensure that the heaters are reliable and safe for use in industrial applications.