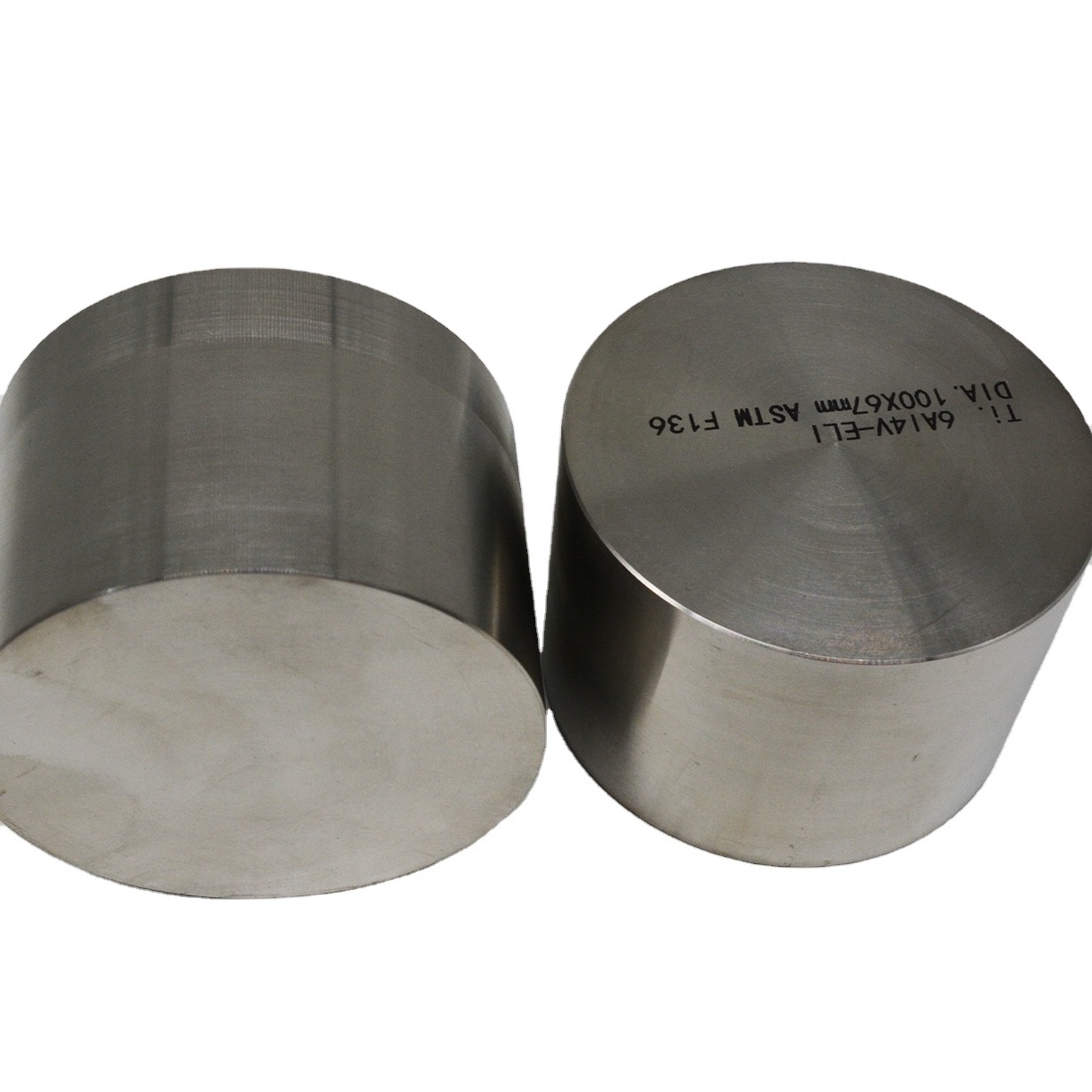
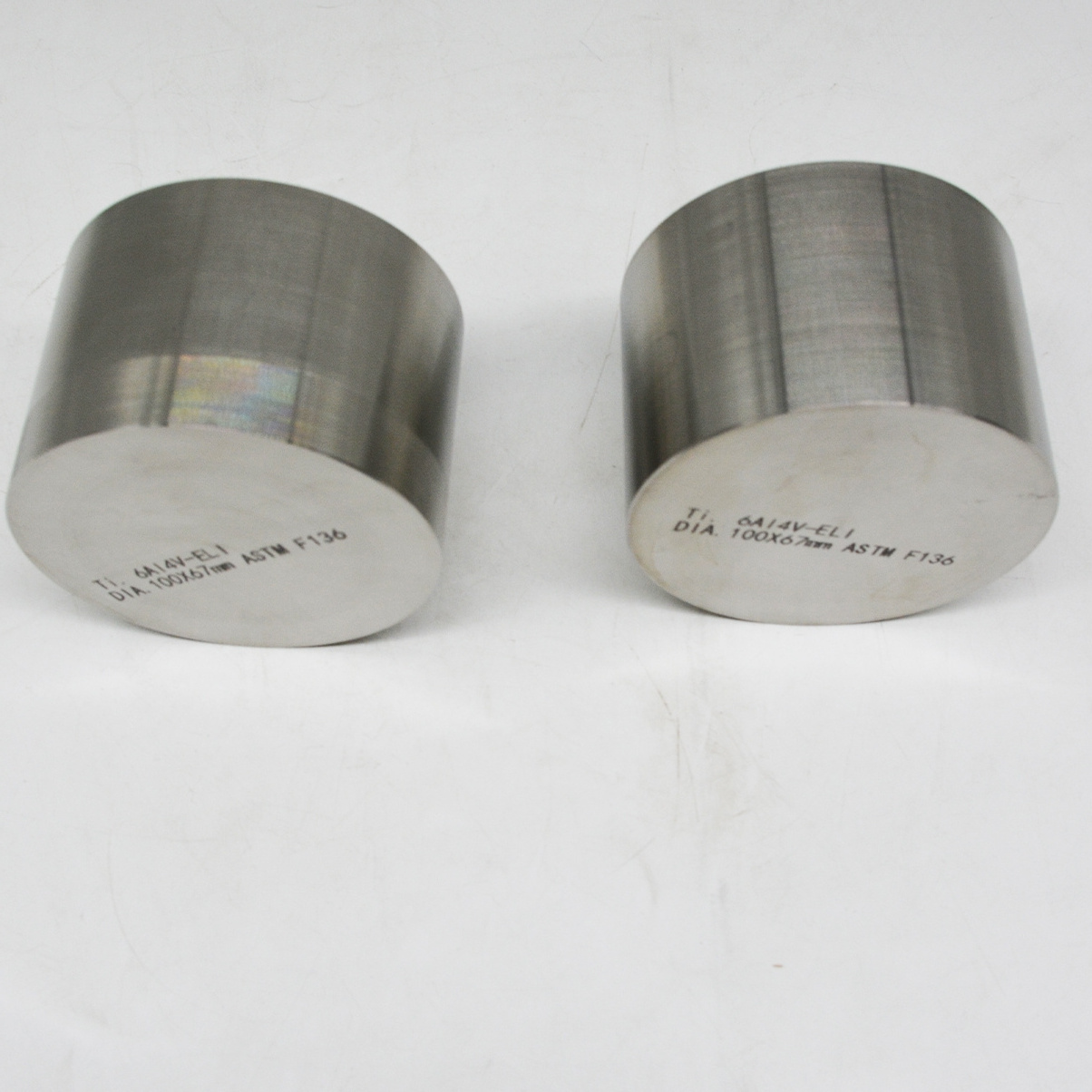
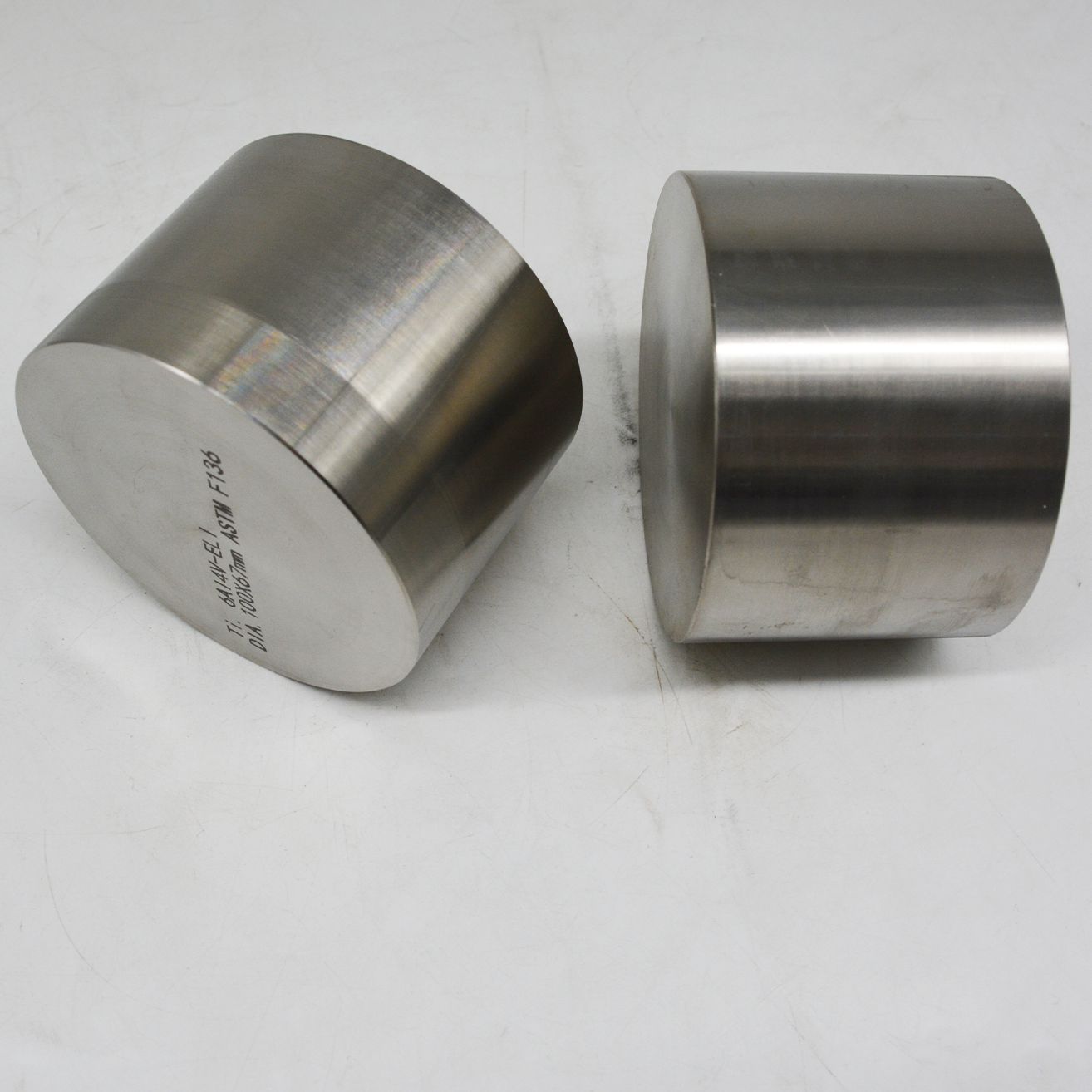
- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
Henan
-
Brand Name:
-
Youbo
-
Model Number:
-
Gr1,Gr2,Gr5
-
Grade:
-
titanium, Gr1,Gr2,Gr5
-
weight:
-
Actual Weight
-
Product name:
-
titanium rod
-
Material:
-
Titaniumm
-
Surface:
-
Machined
-
MOQ:
-
1kg
-
Density:
-
4.51kg/cm3
-
Package:
-
Wooden Case
-
Size:
-
Dia5-300*6000mm
-
Diameter:
-
5-300mm
Quick Details
-
Application:
-
Mechanical equipment
-
Length:
-
6000mm
-
Technique:
-
Forged
-
Place of Origin:
-
Henan
-
Brand Name:
-
Youbo
-
Model Number:
-
Gr1,Gr2,Gr5
-
Grade:
-
titanium, Gr1,Gr2,Gr5
-
weight:
-
Actual Weight
-
Product name:
-
titanium rod
-
Material:
-
Titaniumm
-
Surface:
-
Machined
-
MOQ:
-
1kg
-
Density:
-
4.51kg/cm3
-
Package:
-
Wooden Case
-
Size:
-
Dia5-300*6000mm
-
Diameter:
-
5-300mm
Product description
Properties
A metallic element, titanium is recognized for its high strength-to-weight ratio. It is a strong metal with low density that is
quite ductile (especially in an oxygen-free environment),lustrous, and metallic-white in color. The relatively high melting point
(more than 1,650 °C or 3,000 °F) makes it useful as a refractory metal. It is paramagnetic and has fairly low electrical and
thermal conductivity.
Commercial (99.2% pure) grades of titanium have ultimate tensile strength of about 434 MPa (63,000 psi), equal to that of common,
low-grade steel alloys, but are less dense. Titanium is 60% denser than aluminium, but more than twice as strong as the most
commonly used 6061-T6 aluminium alloy. Certain titanium alloys (e.g., Beta C) achieve tensile strengths of over 1400 MPa (200000
psi). However, titanium loses strength when heated above 430 °C (806 °F).
Titanium is not as hard as some grades of heat-treated steel, is non-magnetic and a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
Machining requires precautions, because the material might gall if sharp tools and proper cooling methods are not used. Like those
made from steel, titanium structures have a fatigue limit that guarantees longevity in some applications. Titanium alloys have
less stiffness than many other structural materials such as aluminium alloys and carbon fiber.
The metal is a dimorphic allotrope of an hexagonal α form that changes into a body-centered cubic (lattice) β form at 882 °C
(1,620 °F). The specific heat of the α form increases dramatically as it is heated to this transition temperature but then falls
and remains fairly constant for the β form regardless of temperature.Similar to zirconium and hafnium, an additional omega phase
exists, which is thermodynamically stable at high pressures, but is metastable at ambient pressures. This phase is usually
hexagonal (ideal) or trigonal (distorted) and can be considered to be due to a soft longitudinal acoustic phonon of the β phase
causing collapse of planes of atoms.
Like aluminium and magnesium, titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air. Titanium readily reacts with
oxygen at 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) in air, and at 610 °C (1,130 °F) in pure oxygen, forming titanium dioxide. It is, however, slow to
react with water and air at ambient temperatures because it forms a passive oxide coating that protects the bulk metal from
further oxidation.When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but continues to grow slowly; reaching a
thickness of 25 nm in four years.
Atmospheric passivation gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum, capable of withstanding
attack by dilute sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, chloride solutions, and most organic acids. However, titanium is corroded by
concentrated acids.As indicated by its negative redox potential, titanium is thermodynamically a very reactive metal that burns in
normal atmosphere at lower temperatures than the melting point. Melting is possible only in an inert atmosphere or in a vacuum. At
550 °C (1,022 °F), it combines with chlorine. It also reacts with the other halogens and absorbs hydrogen.
Titanium is one of the few elements that burns in pure nitrogen gas, reacting at 800 °C (1,470 °F) to form titanium nitride, which
causes embrittlement. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, nitrogen, and some other gases, titanium filaments are applied
in titanium sublimation pumps as scavengers for these gases. Such pumps inexpensively and reliably produce extremely low pressures
in ultra-high vacuum systems.
quite ductile (especially in an oxygen-free environment),lustrous, and metallic-white in color. The relatively high melting point
(more than 1,650 °C or 3,000 °F) makes it useful as a refractory metal. It is paramagnetic and has fairly low electrical and
thermal conductivity.
Commercial (99.2% pure) grades of titanium have ultimate tensile strength of about 434 MPa (63,000 psi), equal to that of common,
low-grade steel alloys, but are less dense. Titanium is 60% denser than aluminium, but more than twice as strong as the most
commonly used 6061-T6 aluminium alloy. Certain titanium alloys (e.g., Beta C) achieve tensile strengths of over 1400 MPa (200000
psi). However, titanium loses strength when heated above 430 °C (806 °F).
Titanium is not as hard as some grades of heat-treated steel, is non-magnetic and a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
Machining requires precautions, because the material might gall if sharp tools and proper cooling methods are not used. Like those
made from steel, titanium structures have a fatigue limit that guarantees longevity in some applications. Titanium alloys have
less stiffness than many other structural materials such as aluminium alloys and carbon fiber.
The metal is a dimorphic allotrope of an hexagonal α form that changes into a body-centered cubic (lattice) β form at 882 °C
(1,620 °F). The specific heat of the α form increases dramatically as it is heated to this transition temperature but then falls
and remains fairly constant for the β form regardless of temperature.Similar to zirconium and hafnium, an additional omega phase
exists, which is thermodynamically stable at high pressures, but is metastable at ambient pressures. This phase is usually
hexagonal (ideal) or trigonal (distorted) and can be considered to be due to a soft longitudinal acoustic phonon of the β phase
causing collapse of planes of atoms.
Like aluminium and magnesium, titanium metal and its alloys oxidize immediately upon exposure to air. Titanium readily reacts with
oxygen at 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) in air, and at 610 °C (1,130 °F) in pure oxygen, forming titanium dioxide. It is, however, slow to
react with water and air at ambient temperatures because it forms a passive oxide coating that protects the bulk metal from
further oxidation.When it first forms, this protective layer is only 1–2 nm thick but continues to grow slowly; reaching a
thickness of 25 nm in four years.
Atmospheric passivation gives titanium excellent resistance to corrosion, almost equivalent to platinum, capable of withstanding
attack by dilute sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, chloride solutions, and most organic acids. However, titanium is corroded by
concentrated acids.As indicated by its negative redox potential, titanium is thermodynamically a very reactive metal that burns in
normal atmosphere at lower temperatures than the melting point. Melting is possible only in an inert atmosphere or in a vacuum. At
550 °C (1,022 °F), it combines with chlorine. It also reacts with the other halogens and absorbs hydrogen.
Titanium is one of the few elements that burns in pure nitrogen gas, reacting at 800 °C (1,470 °F) to form titanium nitride, which
causes embrittlement. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, nitrogen, and some other gases, titanium filaments are applied
in titanium sublimation pumps as scavengers for these gases. Such pumps inexpensively and reliably produce extremely low pressures
in ultra-high vacuum systems.
|
Grade
|
Manufacturing
|
State
|
Diameter (mm)
|
||
|
Gr1 Gr2
Gr3 Gr4
Gr6 Gr7
Gr12
Gr2 Gr3
Gr4 Gr5
Gr6 Gr7
|
1.hot-forging
2.hot-press
3.hot-rolled
4.hot-5.forging+machine(grind)
6.hot-press+machine(grind)
7.hot-rolled+machined (grind)
8. cold-rolling
9.cold-drawing
|
1. R
2. Y
3. M
|
1.hot-forging:
Φ8~200
2.hot-press:
Φ15~18
3.Hot-rolled:Φ8-120
4.cold-rolling
5.cold-drawing:Φ8-~20
|
||
|
Standard
|
ASTM B348
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Product display




Related products
Hot-sale Products
About us
Why Choose Us
Luoyang Youbo Metal Material Co., Ltd.
Luoyang Youbo Metal Material Co., Ltd. is a RMB 5 million joint-stock enterprise. Our company is specialized in producing and exporting non-ferrous metal materials such as tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, tantalum, niobium, as well as alloy products.
With sophisticated equipment, advanced technology, excellent talents and good reputation, our company has established one-stop production line from powder production to bars, rods, wires, plates,etc. Relying on excellent product quality and our good service attitude, our products sell well in domestic and overseas markets such as Korea, Japan, America, Russia, Britain, Germany ,Singapore,etc.And it also helps our company win the high praise from our customers.
Our company has a young, energetic, innovative and hard-working team, who always try our best to achieve good quality, reasonable price, timely delivery.
Based on the policy of equality, mutual benefit and win-win, our company is willing to cooperate with new and old customers at home and abroad to seek both development.
Packing & Delivery
FAQ
What Information Should i Let You Know If I Want To Get A Quotation?
The required material dimension (Thickness*Width*Length,diameter*length; if possible, please kindly supply us drawings).
The required more information, such as Surface Condition, Tolerance Request, The Quantity, and other mechanical and technical
details.
If it is possible, please also provide the application of products, we will recommend the most suitable products with details for
confirmation.
The required more information, such as Surface Condition, Tolerance Request, The Quantity, and other mechanical and technical
details.
If it is possible, please also provide the application of products, we will recommend the most suitable products with details for
confirmation.
How Do You Gurantee The Quality Of The Products?
Each step of production and finished products will be carried out inspection by QC department before storing in the warehouse. NG
goods are not allowed in the completed goods warehouse.
goods are not allowed in the completed goods warehouse.
Can You Guarantee The Prompt Delivery?
Yes, when we get your inquiries, not only we will evaluate the more competitive price, but also we can get the most reasonable
delivery time. So the prompt delivery can be guaranteed.
delivery time. So the prompt delivery can be guaranteed.
What Is The Shipping Cost?
The shipping cost is determined by the destination port, weight, packing size, total CBM of the products, we will try best to get
the most reasonable shipping cost from the forwarders or express couriers to help you save more money.
the most reasonable shipping cost from the forwarders or express couriers to help you save more money.
What Is The Transportation Way?
If the Gross Weight ≤45kg, it’s better by express such as TNT, DHL, FedEx,, etc.
If the Gross Weight between 45kg to 100kg, by express or by air to your nearest airport can be both considered.
If the Gross Weight ≥ 100kg ,you can choose by Air or Sea to the nearest port.
If the Gross Weight between 45kg to 100kg, by express or by air to your nearest airport can be both considered.
If the Gross Weight ≥ 100kg ,you can choose by Air or Sea to the nearest port.
What Is The Size Of Your Tungsten Products?
For tungsten wire, the diameter is from 0.008mm~3.2mm.
For tungsten rod, the diameter is from 2mm~100mm, length is from 50mm~2000mm.
For tungsten sheet, the thickness is from 0.025mm~2mm, the width is from 50mm~500mm, the max length is1000mm.
For tungsten plate, the thickness is from 2.1~25mm, the width is from 30mm~600mm, the max length is 1000mm.
For tungsten boat, the thickness is from 0.2mm~0.5mm, the width is from 5mm~25mm, the max length is 1000mm.
For tungsten tube, the diameter is from 25mm~340mm, the max length is 650mm.
For tungsten crucible,the diameter is from 10mm~500mm, the height is from 10mm~750mm, the thickness is from 2mm~20mm.
For tungsten rod, the diameter is from 2mm~100mm, length is from 50mm~2000mm.
For tungsten sheet, the thickness is from 0.025mm~2mm, the width is from 50mm~500mm, the max length is1000mm.
For tungsten plate, the thickness is from 2.1~25mm, the width is from 30mm~600mm, the max length is 1000mm.
For tungsten boat, the thickness is from 0.2mm~0.5mm, the width is from 5mm~25mm, the max length is 1000mm.
For tungsten tube, the diameter is from 25mm~340mm, the max length is 650mm.
For tungsten crucible,the diameter is from 10mm~500mm, the height is from 10mm~750mm, the thickness is from 2mm~20mm.
Hot Searches