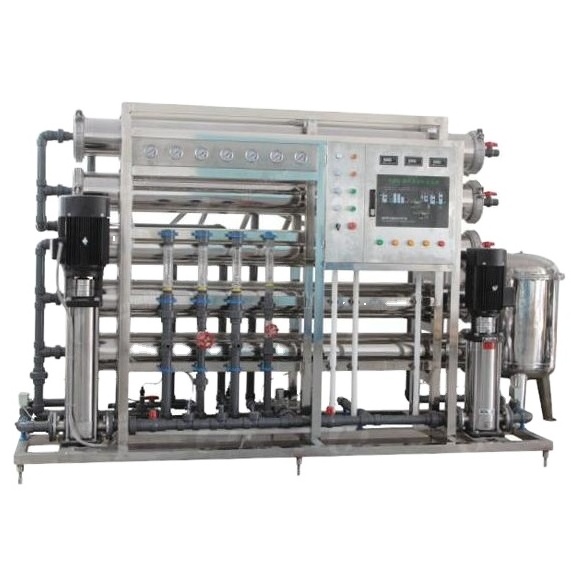
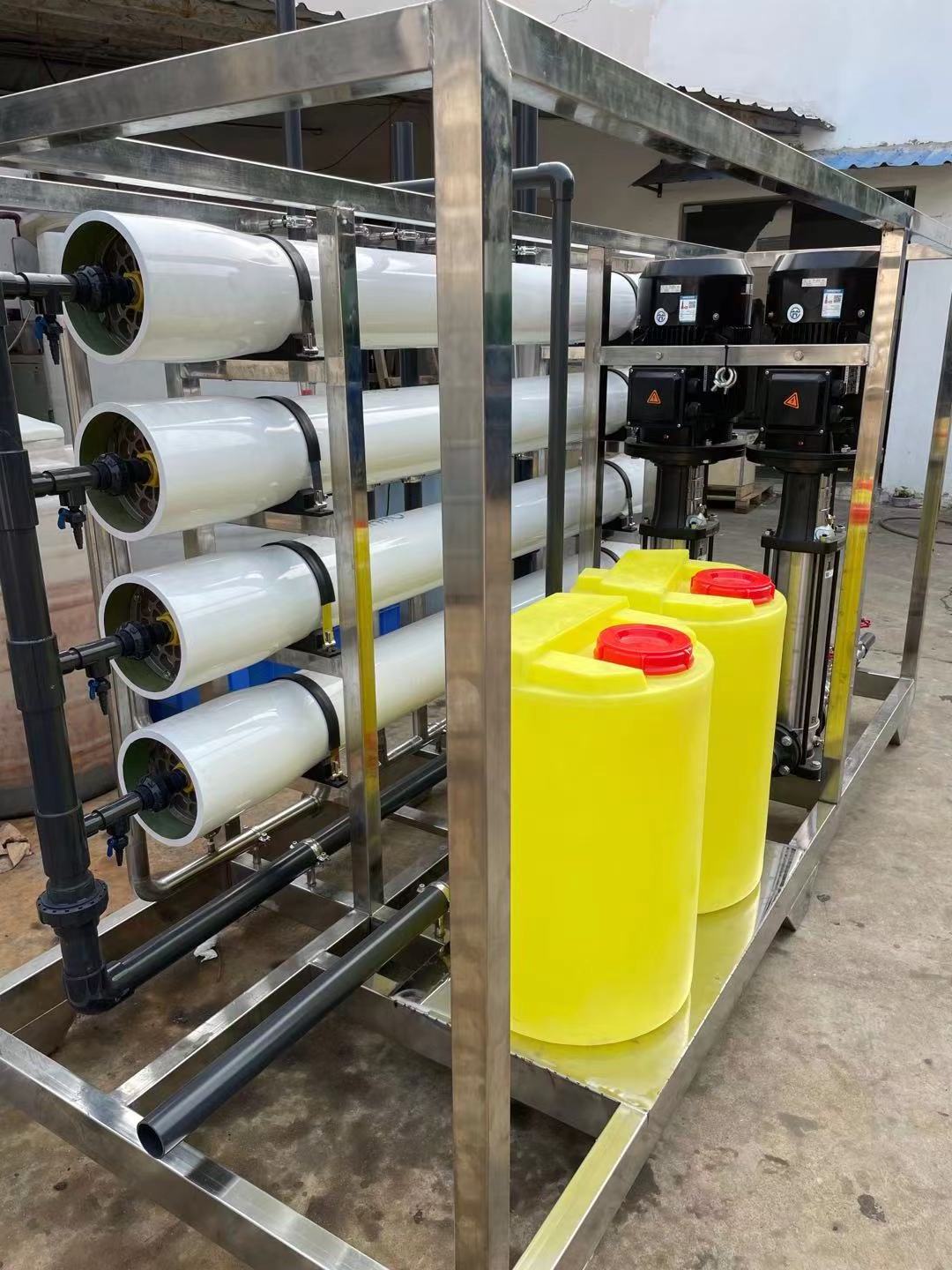
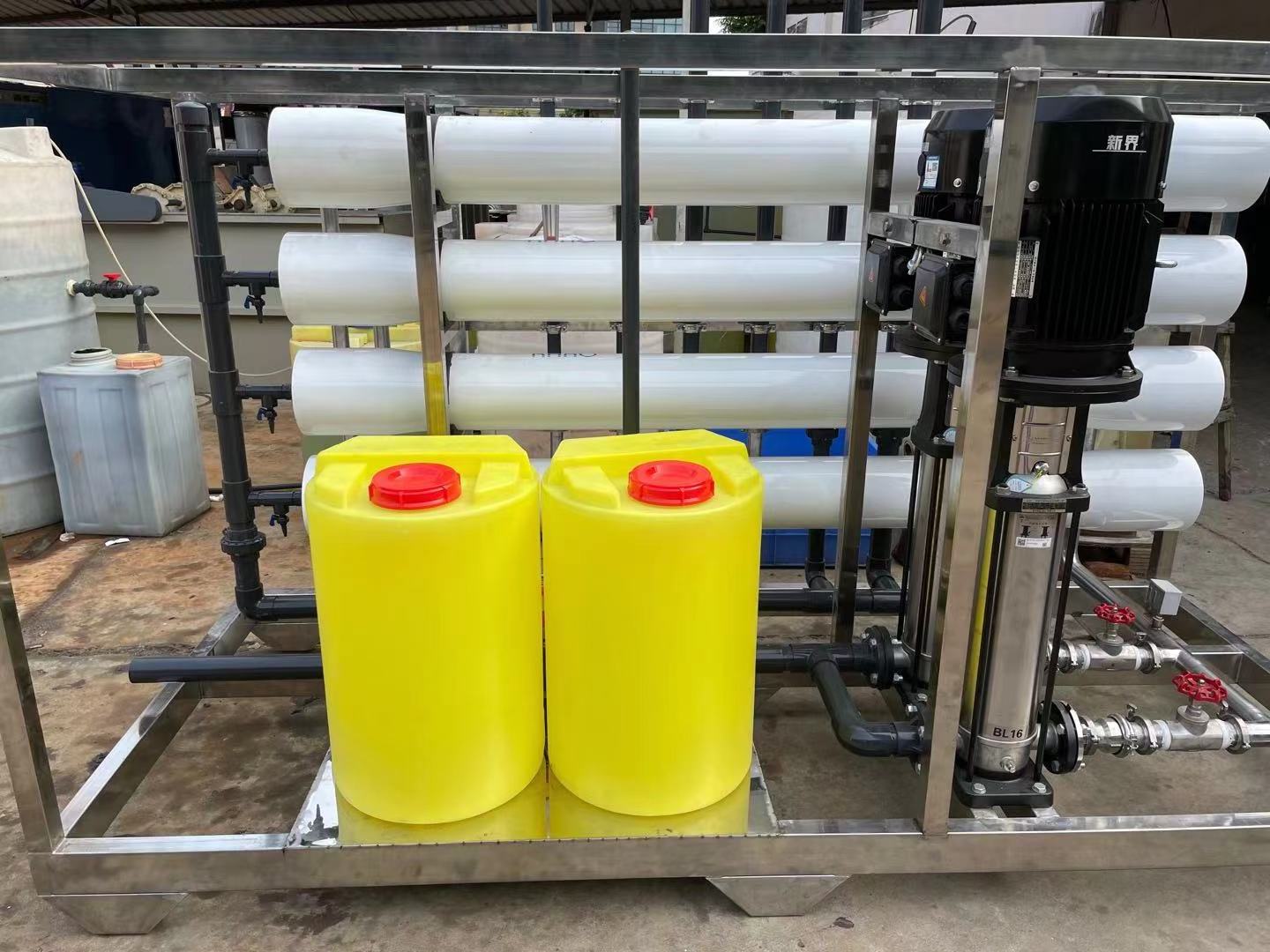
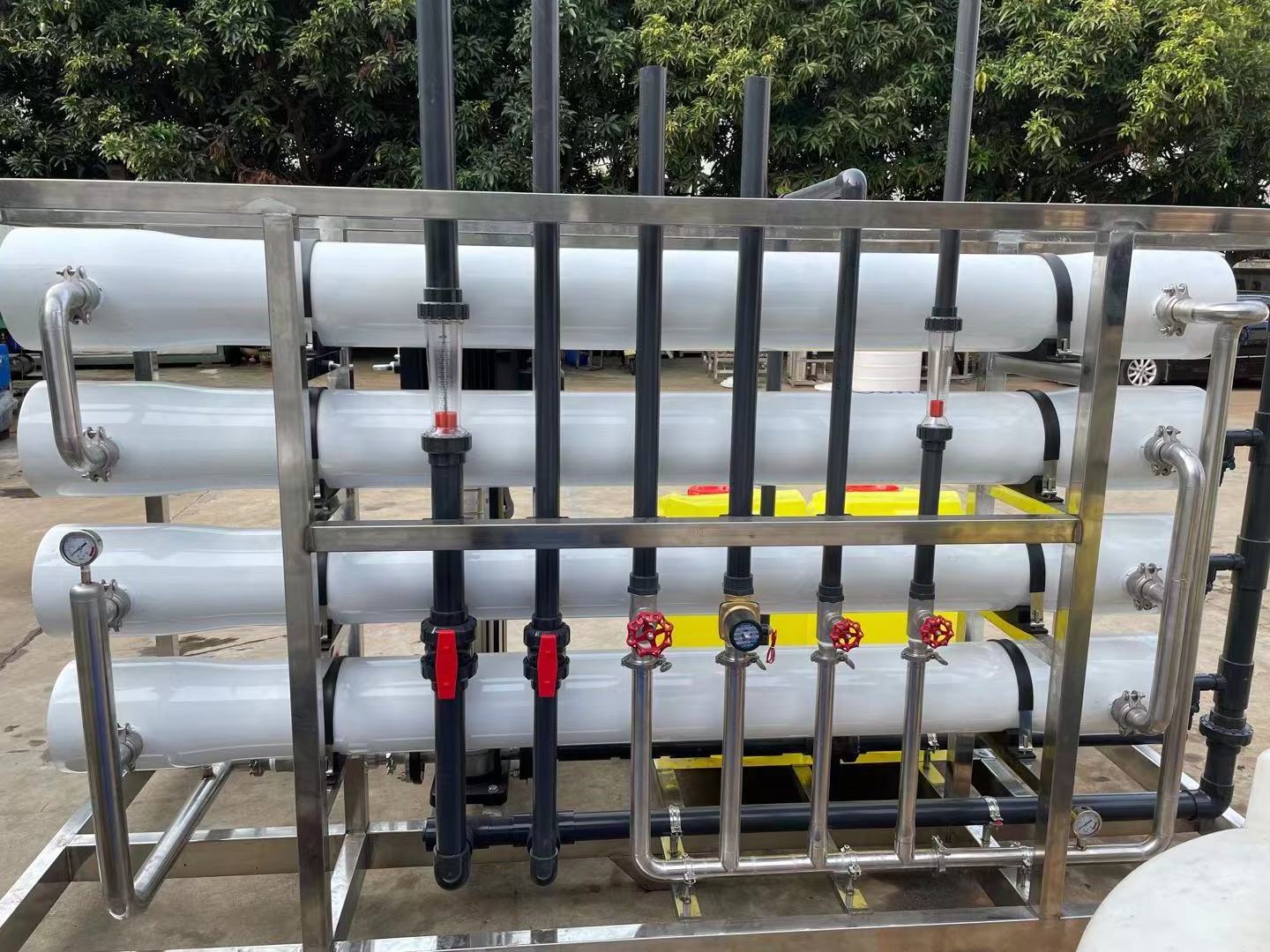
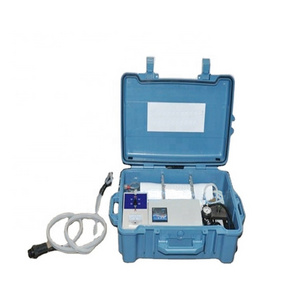
- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Weight:
-
customization
-
Size:
-
customization
-
Productivity:
-
200TD
-
Weight (KG):
-
2500 kg
-
Function:
-
seawater desalination
-
Product name:
-
SWRO plant
-
Capacity:
-
200T/D
-
RO Membrane:
-
MR-SW-8040
-
Certification:
-
CE Certificate
-
Processing:
-
Pre-treatment+RO Desaliantion
-
Technology:
-
pretreatment+SWRO
-
Voltage:
-
380V /Customized
-
Production capacity:
-
10TH
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
China
-
Brand Name:
-
MR
-
Material:
-
customization
-
Weight:
-
customization
-
Size:
-
customization
-
Productivity:
-
200TD
-
Weight (KG):
-
2500 kg
-
Function:
-
seawater desalination
-
Product name:
-
SWRO plant
-
Capacity:
-
200T/D
-
RO Membrane:
-
MR-SW-8040
-
Certification:
-
CE Certificate
-
Processing:
-
Pre-treatment+RO Desaliantion
-
Technology:
-
pretreatment+SWRO
-
Voltage:
-
380V /Customized
-
Production capacity:
-
10TH
Product Description
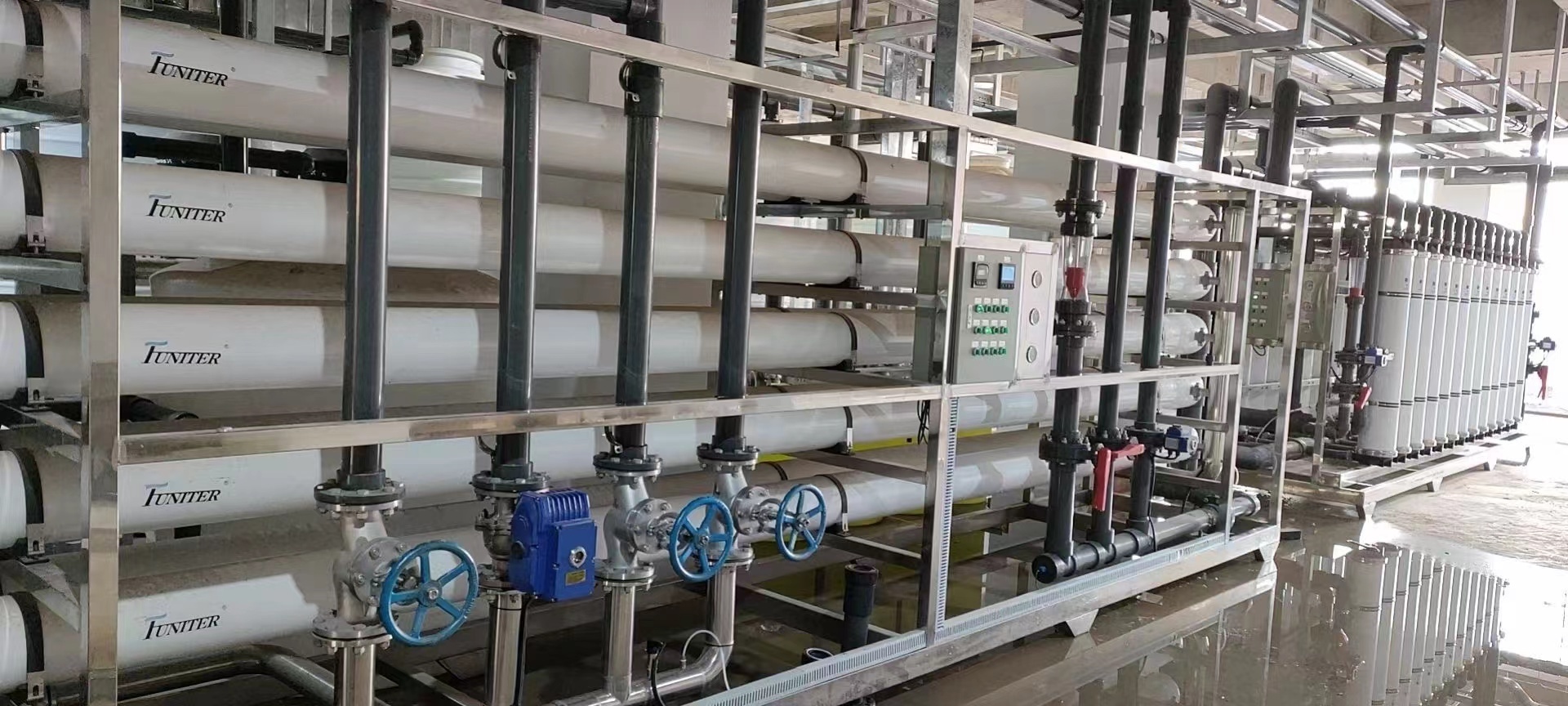
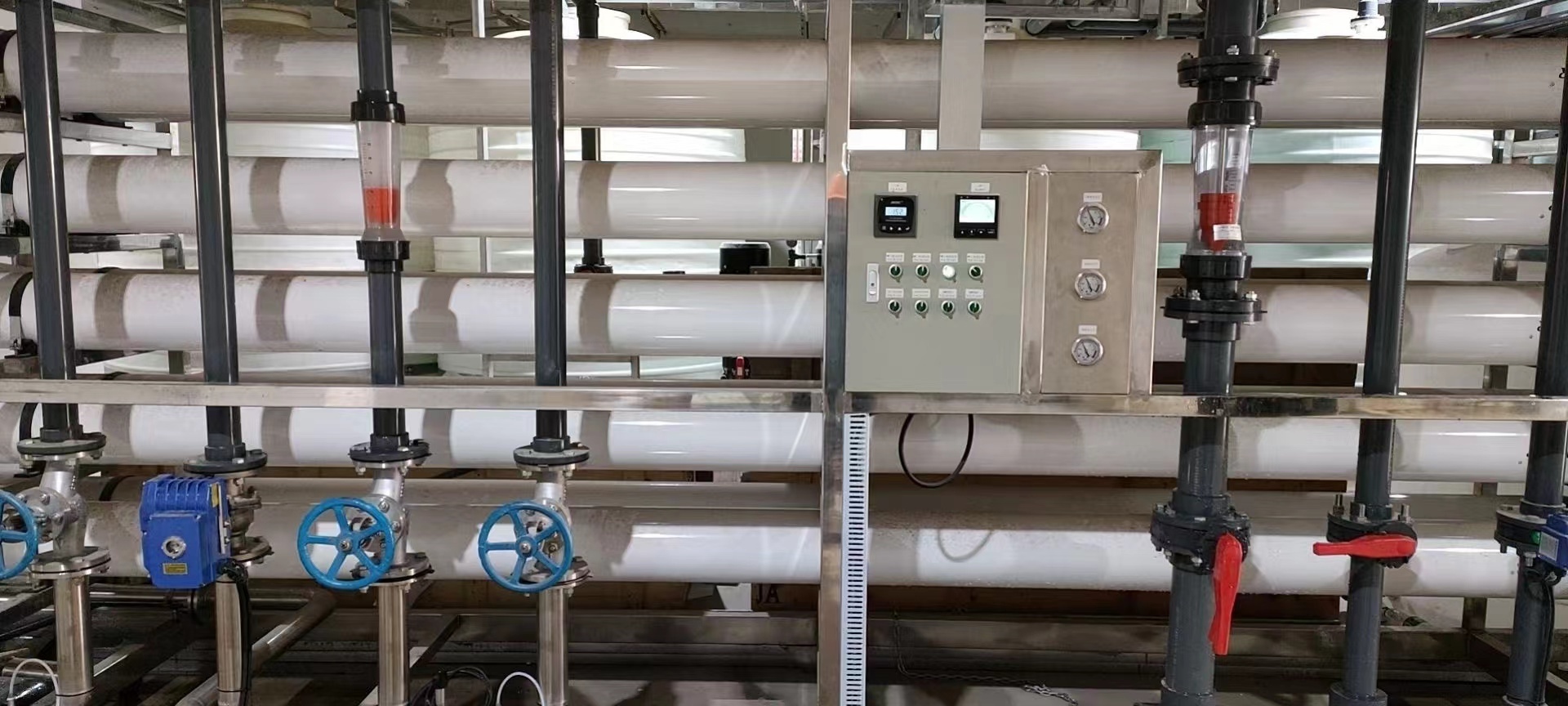


|
Model
|
Produced water
|
Power consume
|
recovery rate
|
salt reject rate
|
|
MR-SW-1000L
|
1000LPH
|
2.2kw
|
55%
|
98%
|
|
MR-SW-2000L
|
2000LPH
|
3kw
|
60%
|
98%
|
|
MR-SW-3000L
|
3000LPH
|
4.5kw
|
60%
|
98%
|
|
MR-SW-10T
|
10TH
|
15KW
|
60%
|
98%
|
|
MR-SW-20T
|
20TH
|
22KW
|
60%
|
99%
|
|
MR-SW-30T
|
30TH
|
26KW
|
60%
|
99%
|
|
MR-SW-50T
|
50TH
|
55KW
|
60%
|
99%
|
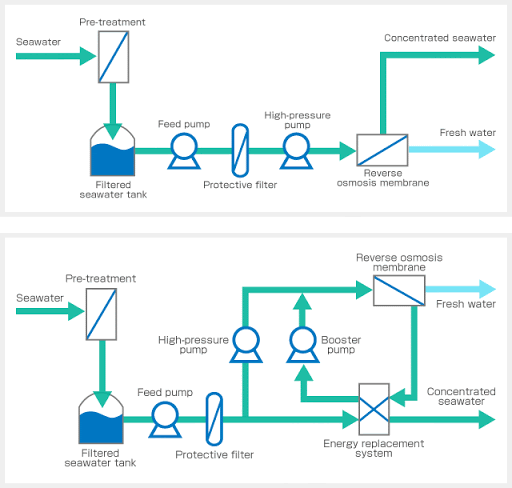
SWRO
Pretreatment
Pretreatment is important when working with reverse osmosis membranes due to the nature of their spiral wound design. For SWRO
pretreatment has four major components.
• multimedia filtration
• cartridge filtration
• chemical dosing (smbs, antiscalant...)
• pH adjustment
Pretreatment
Pretreatment is important when working with reverse osmosis membranes due to the nature of their spiral wound design. For SWRO
pretreatment has four major components.
• multimedia filtration
• cartridge filtration
• chemical dosing (smbs, antiscalant...)
• pH adjustment
High Pressure Pump
The high pressure pump supplies the pressure needed to push water through the membranes, even as the membrane rejects the passage of salt through it. For SWRO system pressure required is changing from 30 bar to 80 bars.
Membrane Assembly
The membrane assembly consists of a pressure vessel with a membrane that allows feedwater to be pressed against it. The membrane must be strong enough to withstand whatever pressure is applied against it. Reverse osmosis membranes are made in a variety of configurations, with the two most common configurations being spiral-wound and hollow-fiber.
Only a part of the saline feed water pumped into the membrane assembly passes through the membrane with the salt removed. The remaining "concentrate" flow passes along the saline side of the membrane to flush away the concentrated salt solution.
The percentage of desalinated water produced versus the saline water feed flow is known as the "recovery ratio".
This varies with the salinity of the feed water and the system design parameters: typically 20% for small seawater systems, 40% –50% for larger seawater systems, and 80% – 85% for brackish water.The concentrate flow is at typically only 3 bar / 50 psi less than the feed pressure, and thus still carries much of the highpressure pump input energy.
Energy Recovery
Energy recovery can reduce energy consumption by 50% or more. Much of the high pressure pump input energy can be recovered from
the concentrate flow, and the increasing efficiency of energy recovery devices has greatly reduced the energy needs of reverse osmosis desalination. Devices used, in order of invention, are:
• Turbine or Pelton wheel: a water turbine driven by the concentrate flow, connected to the HPP drive shaft to provide part of itsinput power. Positive displacement axial piston motors have also been used in place of turbines on smaller systems.
• Turbocharger: a water turbine driven by the concentrate flow, directly connected to a centrifugal pump which boosts the high pressure pump output pressure, reducing the pressure needed from the high pressure pump and thereby its energy input, similar in construction principle to car engine turbochargers.
• Pressure exchanger: using the pressurized concentrate flow, in direct contact or via a piston, to pressurize part of the
membrane feed flow to near concentrate flow pressure. A boost pump then raises this pressure by typically 3 bar / 50 psi to the membrane feed pressure. This reduces flow needed from the high-pressure pump by an amount equal to the concentrate flow, typically 60%, and thereby its energy input. These are widely used on larger low-energy systems. They are capable of 3 kWh/m3 or less energy consumption.
The high pressure pump supplies the pressure needed to push water through the membranes, even as the membrane rejects the passage of salt through it. For SWRO system pressure required is changing from 30 bar to 80 bars.
Membrane Assembly
The membrane assembly consists of a pressure vessel with a membrane that allows feedwater to be pressed against it. The membrane must be strong enough to withstand whatever pressure is applied against it. Reverse osmosis membranes are made in a variety of configurations, with the two most common configurations being spiral-wound and hollow-fiber.
Only a part of the saline feed water pumped into the membrane assembly passes through the membrane with the salt removed. The remaining "concentrate" flow passes along the saline side of the membrane to flush away the concentrated salt solution.
The percentage of desalinated water produced versus the saline water feed flow is known as the "recovery ratio".
This varies with the salinity of the feed water and the system design parameters: typically 20% for small seawater systems, 40% –50% for larger seawater systems, and 80% – 85% for brackish water.The concentrate flow is at typically only 3 bar / 50 psi less than the feed pressure, and thus still carries much of the highpressure pump input energy.
Energy Recovery
Energy recovery can reduce energy consumption by 50% or more. Much of the high pressure pump input energy can be recovered from
the concentrate flow, and the increasing efficiency of energy recovery devices has greatly reduced the energy needs of reverse osmosis desalination. Devices used, in order of invention, are:
• Turbine or Pelton wheel: a water turbine driven by the concentrate flow, connected to the HPP drive shaft to provide part of itsinput power. Positive displacement axial piston motors have also been used in place of turbines on smaller systems.
• Turbocharger: a water turbine driven by the concentrate flow, directly connected to a centrifugal pump which boosts the high pressure pump output pressure, reducing the pressure needed from the high pressure pump and thereby its energy input, similar in construction principle to car engine turbochargers.
• Pressure exchanger: using the pressurized concentrate flow, in direct contact or via a piston, to pressurize part of the
membrane feed flow to near concentrate flow pressure. A boost pump then raises this pressure by typically 3 bar / 50 psi to the membrane feed pressure. This reduces flow needed from the high-pressure pump by an amount equal to the concentrate flow, typically 60%, and thereby its energy input. These are widely used on larger low-energy systems. They are capable of 3 kWh/m3 or less energy consumption.
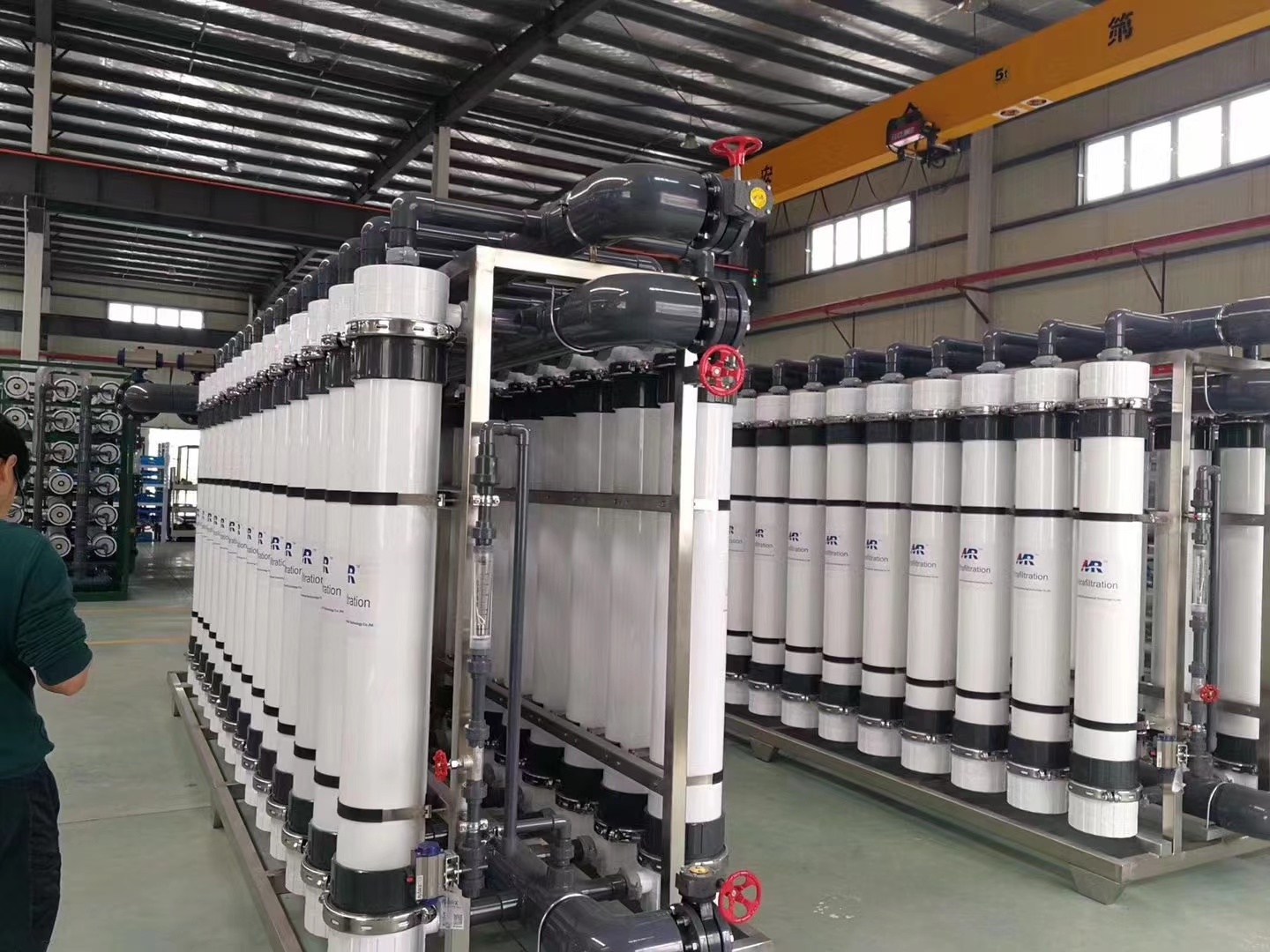

see what we could do
large scale industrial water treatment system including ultrafiltration system,reverse osmosis,integrerated equipment,composite solution for customer
our project
we mainly serve for industrial park,local government,public organization
our factory
twelve factorys local in different provinces in China
Hot Searches