- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
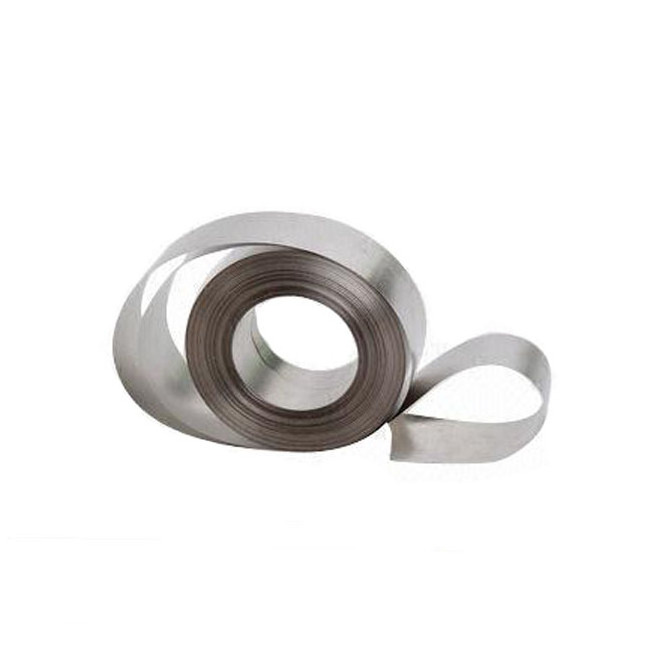
Quick Details
-
Ribbon width:
-
5mm~80mm
-
Ribbon thickness:
-
18mm~30mm
-
Saturation magnetic:
-
1.56T
-
Density:
-
7.18g/cm3
-
OEM&ODM:
-
Acceptable
-
Material:
-
Fe-based amrphous
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
Guangdong, China
-
Magnetic Materials:
-
soft magnetic materials
-
Product name:
-
Amorphous Ribbon
-
Ribbon width:
-
5mm~80mm
-
Ribbon thickness:
-
18mm~30mm
-
Saturation magnetic:
-
1.56T
-
Density:
-
7.18g/cm3
-
OEM&ODM:
-
Acceptable
-
Material:
-
Fe-based amrphous

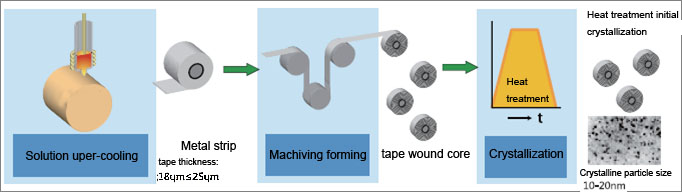
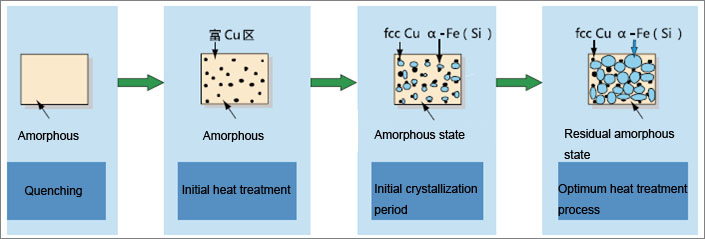
The nanocrystalline alloy is added with a trace amount of elements such as Cu and Nb on the basis of the Fe-Si-B alloy composition, and is prepared into an amorphous ribbon by an ultra-cold solidification technique with a cooling rate of about 106/sec. The amorphous ribbon is heat treated above the crystallization temperature to form a nanocrystalline alloy having a grain size of 10-20 nm. Nanocrystalline alloys have more excellent magnetic properties than amorphous.
Nanocrystalline Alloy Manufacture Method :
Nanocrystalline Alloy Crystallization Process:
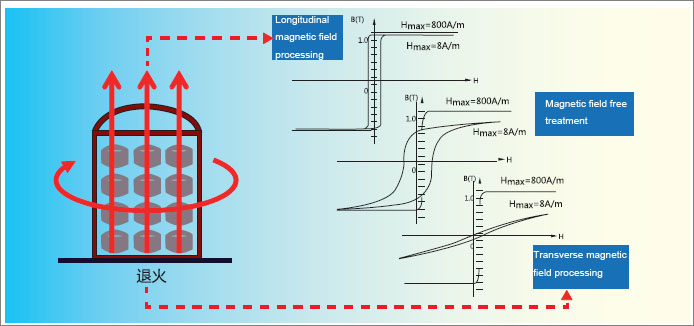
Nanocrystalline Alloy Heat Treatment Process:
Key Properties:
l High saturation magnetic induction
l High initial permeability
l Low Coercivity
l Low lo s s
l Good temperature stability
Nanocrytalline Ribbon Brand No.:
|
No. |
Alloy Brand |
Foreign Brand |
China Brand |
Application |
|
1 |
N26-01 |
Finemet |
1K107 |
Current transformer, micro-internal transformer, zero-sequence current transformer, test port filter inductor, saturable inductor (magnetic amplifier, spike suppressor) |
|
2 |
N26-02 |
|
1K107A |
Common mode inductor, filter inductor, saturable inductor, high power high frequency switching power supply transformer (such as inverter welder power transformer, communication power transformer, high frequency induction heating power transformer, UPS power supply, laser power supply, electrolytic plating power supply), pulse DC leakage protector, DC component transformer, pulse transformer, magnetic shielding |
|
3 |
N26-03 |
|
1K107B |
Common mode inductor, filter inductor, saturable inductor, high power high frequency switching power supply transformer (such as inverter welder power transformer, communication power transformer, high frequency induction heating power transformer, UPS power supply, laser power supply, electrolytic plating power supply), pulse DC leakage protector, DC component transformer, pulse transformer, magnetic shielding |
|
4 |
N26-04 |
|
1K107D |
Current transformer, micro-internal transformer, zero-sequence current transformer, test port filter inductor, DC component transformer |
|
Physical characteristics |
|
|
Density |
ρ = 7.2 g/cm 3 |
|
Electrical Resistivity |
ρ ≥1.3µΩcm |
|
crystallization temperature |
Tx >510 ℃ |
|
Vickers Hardness |
Hv= 880 kg/mm 2 |
|
Lamination Factor |
≥ 0.7 5 |
The nanocrystalline alloy can be subjected to magnetic field treatment according to the needs of the product (transverse magnetic and longitudinal magnetic field treatment),
and the transverse magnetic treatment is performed by applying an external magnetic field along the strip direction for longitudinal heat treatment, that is, applying a magnetic field in the direction of the vertical strip for heat treatment.
The magnetic field-treated nanocrystalline alloy undergoes partial changes in magnetic properties. The specific DC B-H loop is shown in the following table.
Nanocrystalline Strips Alloy Specification :
|
No. |
Product Name |
Robbion Width (mm) |
Torance (mm) |
Ribbon Thickness (µm) |
Strip Condition |
|
|
A |
B |
|||||
|
1 |
N-R26002 |
2 |
±0.1mm |
18~24 |
24~32 |
Direct Injection /Cut |
|
2 |
N-R26003 |
3 |
||||
|
3 |
N-R26005 |
5 |
||||
|
4 |
N-R26006 |
6 |
||||
|
5 |
N-R26008 |
8 |
||||
|
6 |
N-R26010 |
10 |
||||
|
7 |
N-R26015 |
15 |
||||
|
8 |
N-R26020 |
20 |
||||
|
9 |
N-R26025 |
25 |
+0.20/-0.20mm |
|||
|
10 |
N-R26030 |
30 |
||||
|
11 |
N-R26035 |
35 |
||||
|
12 |
N-R26040 |
40 |
||||
|
13 |
N-R26045 |
45 |
+0.20/-0.50mm |
|||
|
14 |
N-R26050 |
50 |
||||
|
Note: Width could be cutting based on client's request, from 2~50mm. |
||||||
he difference between A and B:
A stands for thin belt and B stands for ordinary belt. In addition to the difference in strip thickness, the magnetic field sensitivity of belt A has a certain advantage in terms of iron loss and frequency characteristics. The characteristic comparison curve is as follows :













