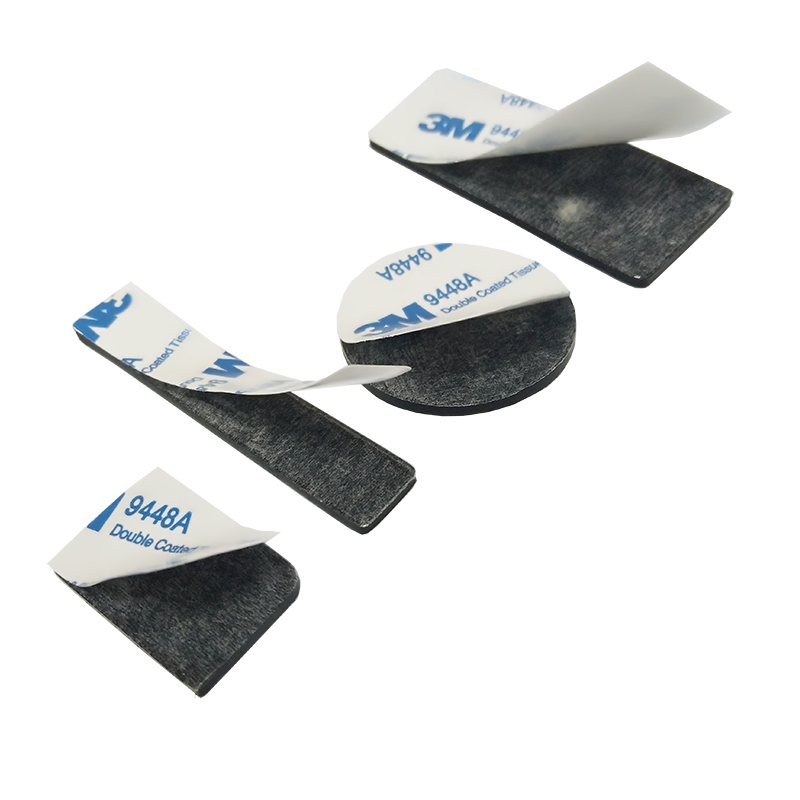
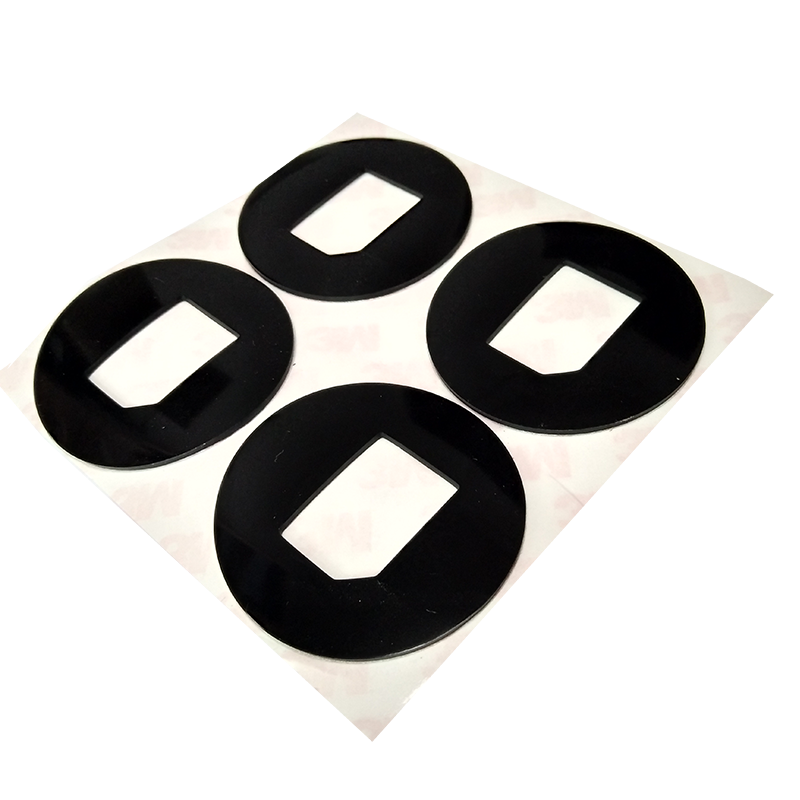
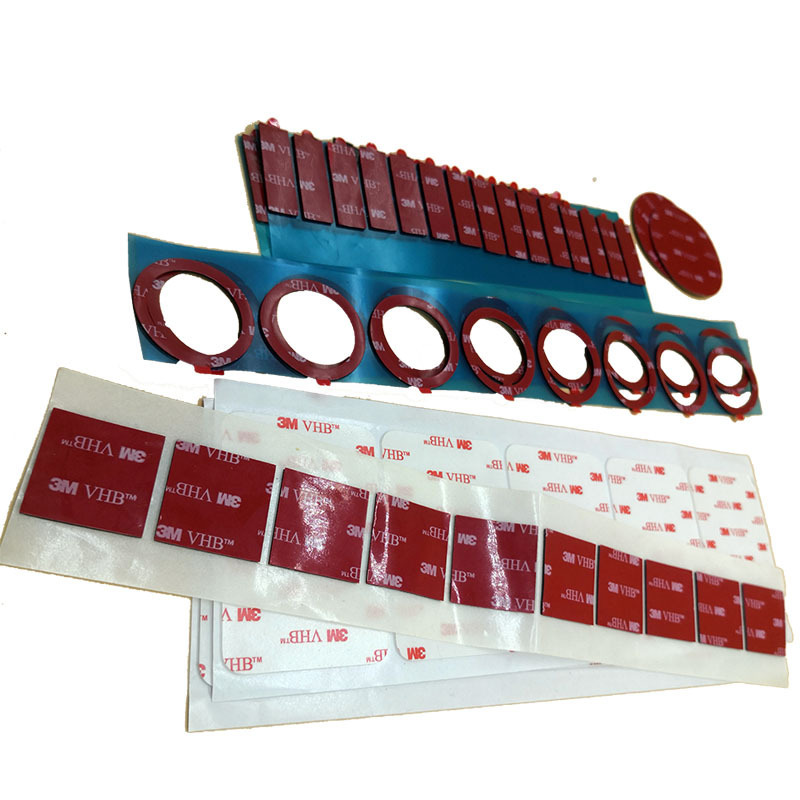
- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Model Number:
-
LS-JL-1A211
-
Material:
-
NBR/EPDM/CR/Butyl
-
Color:
-
Black
-
Thickness:
-
0.3MM~10MM
-
Width:
-
5MM~1000MM
-
Length:
-
10M/33M/50M
-
Liner Color:
-
White/Yellow
-
Adhesive:
-
Silicone/Acrylic
-
Samples:
-
Free
-
Certification:
-
ISO14001&9001
Quick Details
-
Processing Service:
-
Cutting
-
Place of Origin:
-
Guangdong, China
-
Brand Name:
-
LS
-
Model Number:
-
LS-JL-1A211
-
Material:
-
NBR/EPDM/CR/Butyl
-
Color:
-
Black
-
Thickness:
-
0.3MM~10MM
-
Width:
-
5MM~1000MM
-
Length:
-
10M/33M/50M
-
Liner Color:
-
White/Yellow
-
Adhesive:
-
Silicone/Acrylic
-
Samples:
-
Free
-
Certification:
-
ISO14001&9001
Rubber is composed of long chains of randomly oriented molecules. These long chains are subject to entanglement and cross-linking. The entanglement has a significant impact on the viscoelastic properties such as stress relaxation. When a rubber is exposed to stress or strain energy, internal rearrangements such as rotation and extension of the polymer chains occur. These changes occur as a function of the energy applied and the duration and rate of application, as well as the temperature at which the energy is applied.
A rubber is response to an applied energy can be energy storage (elastic) or energy dissipation (viscous). For sealing elastomers, the elastic component of response is most important. An applied stress induces a corresponding strain which creates contact stress (or seal-ing force). As the polymer chains rearrange to reduce this internal energy, or stored force, a loss of sealing force occurs.
Rubber products are typically cured at high temperature and pressure. The addition of curatives and accelerators forms cross-links between the polymer chains or backbone. It is this network of crosslinks that largely determines the physical properties of tensile, elongation and compression set.
Fillers play a large role in rubber technology. Carbon black and silica fillers can serve to improve the hardness, abrasion resistance, tensile properties and tear strength. Non-black fillers, such as titanium dioxide and barium sulphate can offer pigmenting properties for part identification, as well as improved stability in strong oxidizing environments. However, the viscoelastic response and hysteresis losses are greatly enhanced by the use of fillers.




|
Property
|
NBR
|
EPDM
|
Neoprene
|
Silicone
|
|
Tensile Strength
|
Good
|
Excelent
|
Excelent
|
Fair
|
|
Abrasion Resistance
|
Good
|
Excelent
|
Excelent
|
Poor
|
|
Tear Resistance
|
Good
|
Excelent
|
Excelent
|
Poor
|
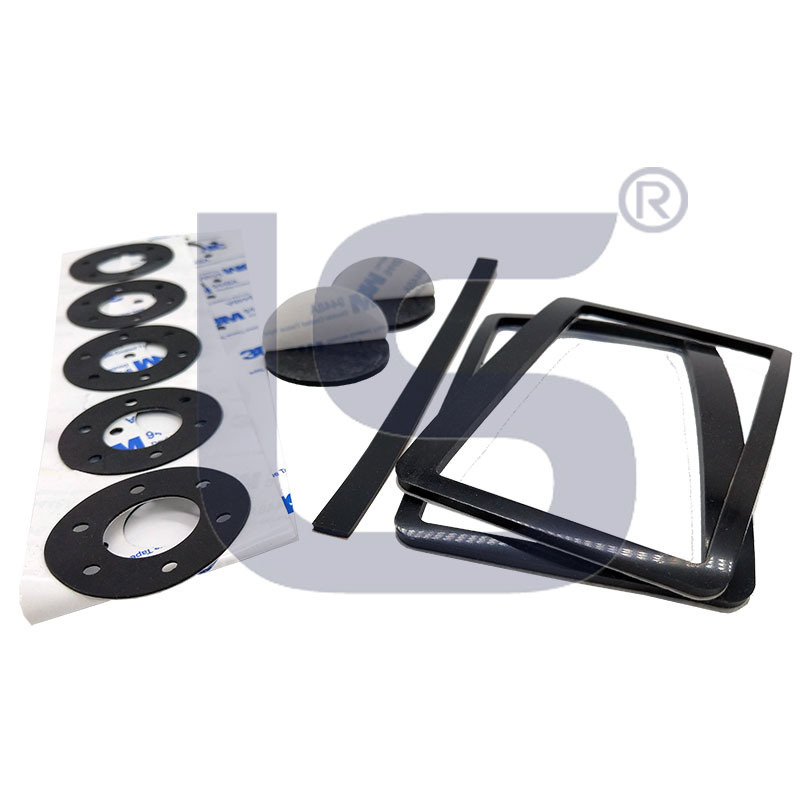
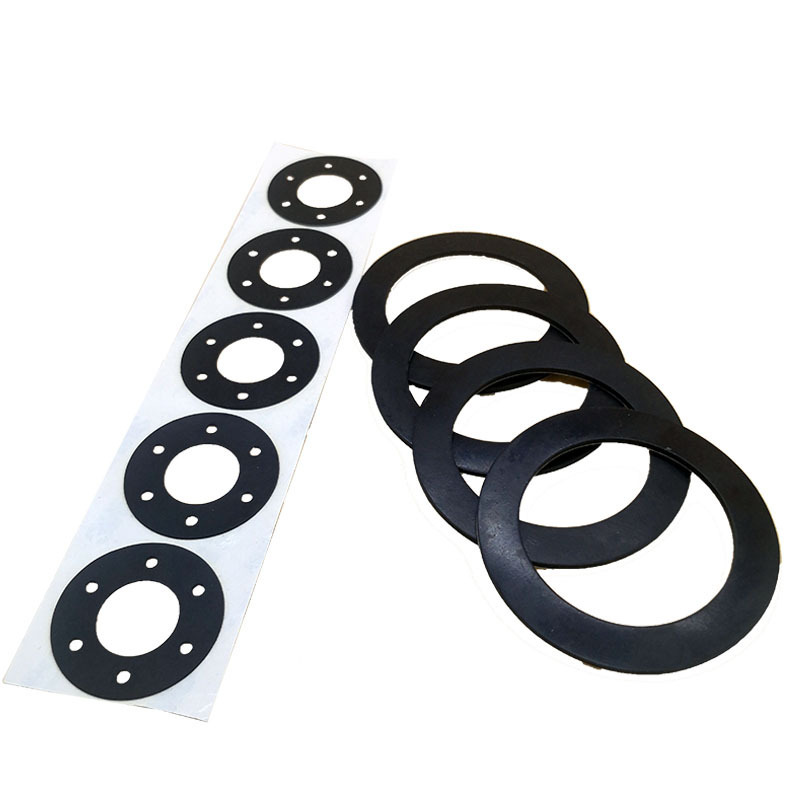
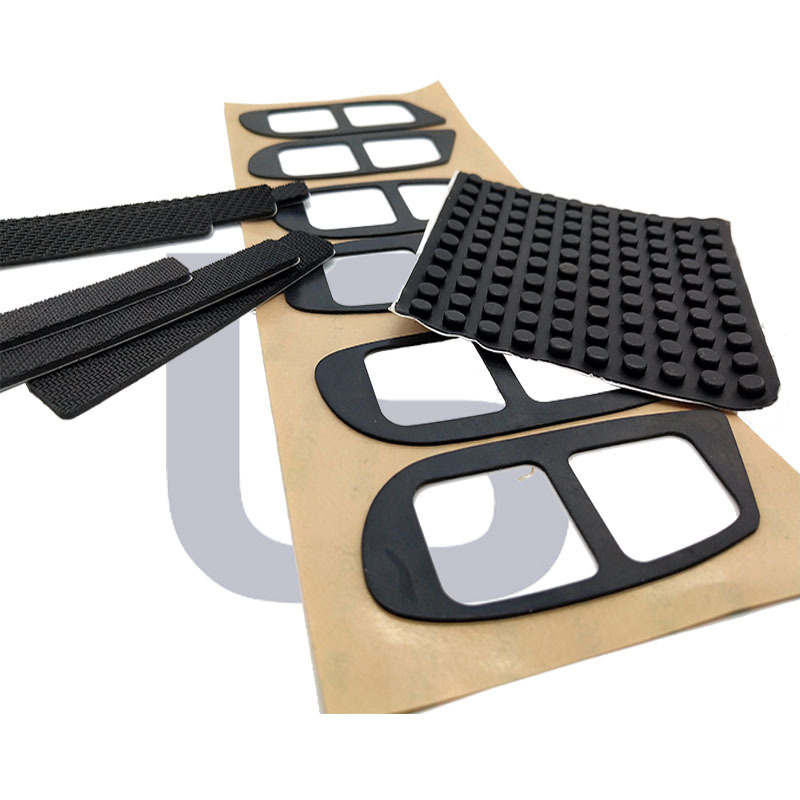
Single/Double Sided Adhesive Rubber Pad

|
Contact
|
Joel Zhao(Sales Manager)
|
|
Email
|
joel
@
szlstape.com
|
|
Phone
|
86-0755-23198762
|
|
Mobile
|
86-135-3783-9200
|
|
Skype
|
joel LSzhao
|
|
Website
|
www.szlstape.com
|