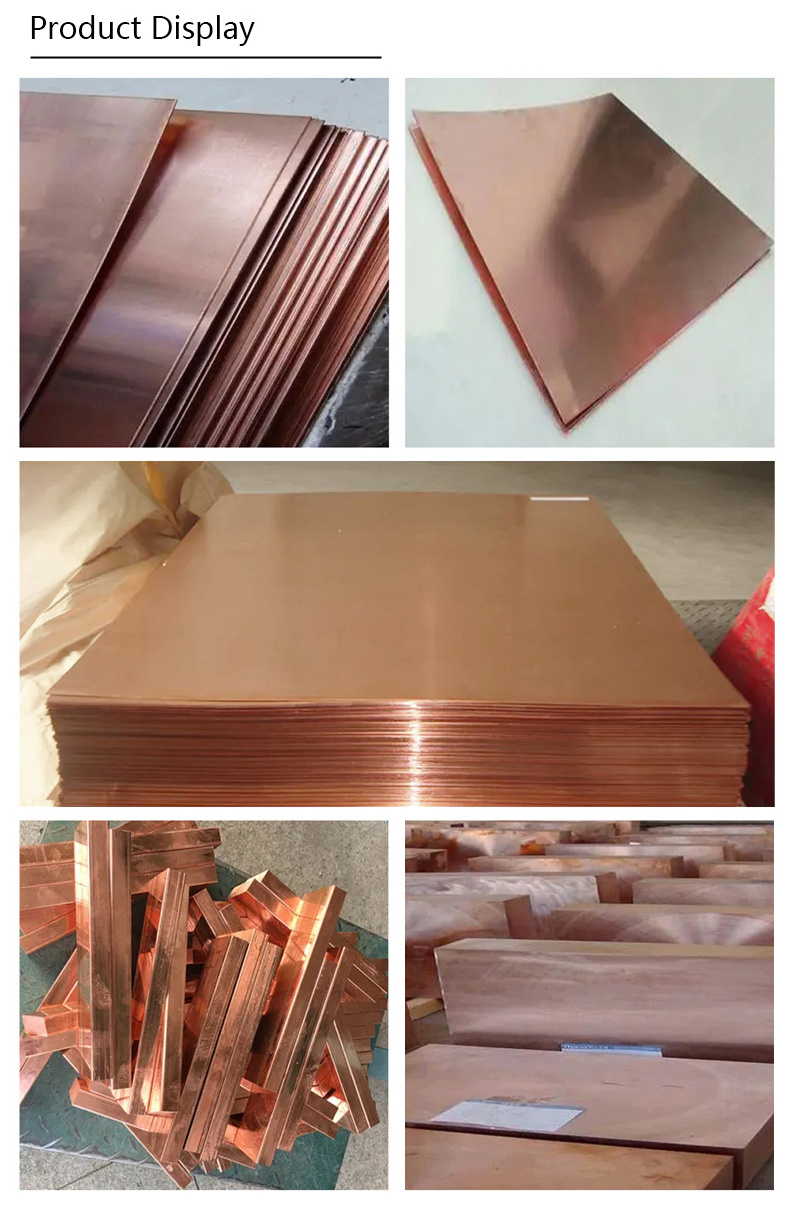
Copper is one of the oldest metals known to mankind, and its applications are vast and varied. From electrical wiring to architectural design, from electronics manufacturing to automotive components, copper plates play an essential role in many industries.
A Brief Description of Copper Plate:
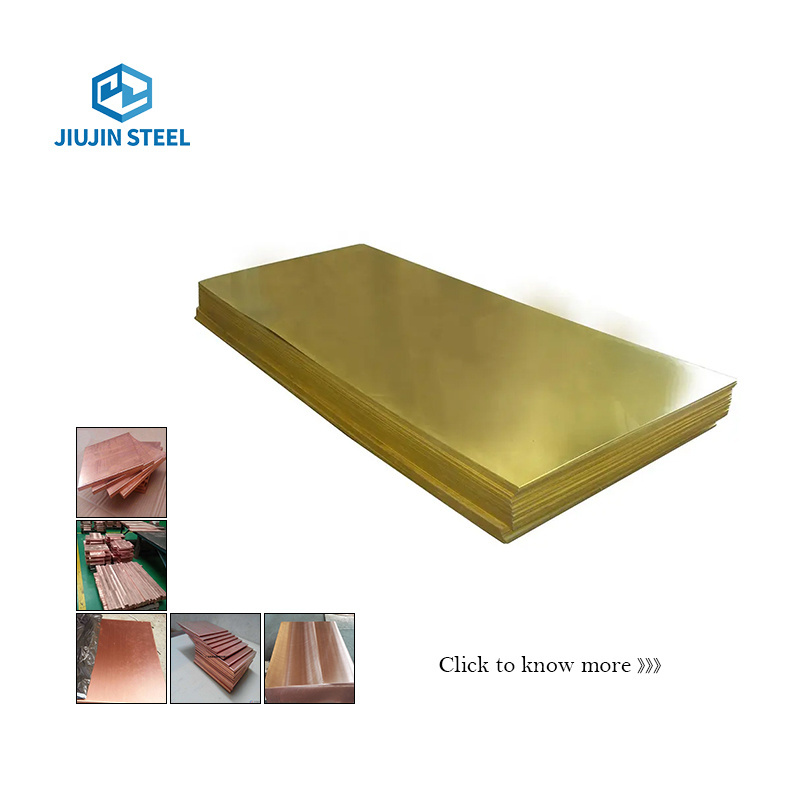
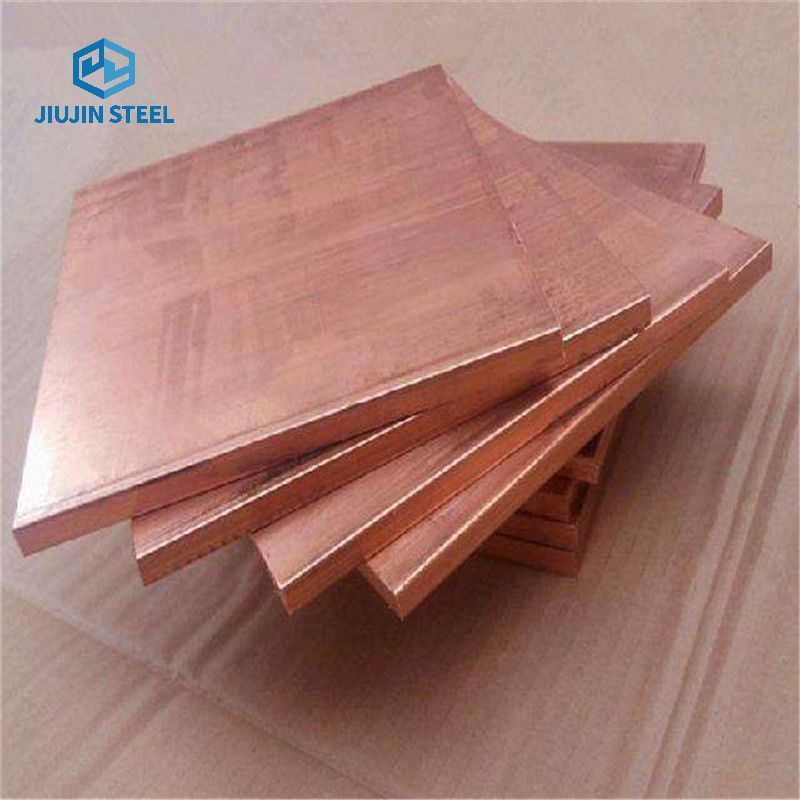
Copper plate is a flat sheet of copper metal that is typically formed through casting or
rolling processes. It is composed primarily of copper, with small amounts of other elements added to enhance specific properties.
Copper plate exhibits excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Its distinctive
reddish-orange hue adds aesthetic appeal to architectural designs while retaining its functional qualities.
Applications of Copper Plate:
Copper plates find extensive usage in several industries due to their unique combination of
properties. Let's explore some common applications:
1. Electrical Industry: Copper plates are widely employed in the electrical industry due to their high electrical conductivity.They are used in electrical wiring systems, power generation, transmission, and distribution networks. The exceptional conductivity of copper ensures efficient and safe transfer of electricity, minimizing energy loss and maximizing performance.
2. Construction Sector: In the construction sector, copper plates are used for roofing, cladding, and architectural
embellishments. Copper's corrosion resistance and durability make it an ideal choice for exterior applications. Over time,copper develops a green patina, which adds a timeless elegance to buildings and structures.
3. Electronics Manufacturing: Copper plates are extensively utilized in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs). The conductivity of copper allows for efficient flow of electric current, while its thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat generated by electronic components. Copper is also highly ductile, allowing it to be shaped into intricate circuits and connections required in modern electronic devices.
4. Automotive Industry: Copper plates play an important role in the automotive industry due to their excellent thermal properties and durability. They are used in radiators, heat exchangers, and electrical components such as connectors and wiring harnesses.Copper's ability to conduct and dissipate heat efficiently helps regulate engine temperature and improve overall performance.
5. Arts and Crafts: Beyond industrial applications, copper plates have a long history in the world of arts and crafts. They serve as a canvas for various artistic techniques such as etching, engraving, and embossing. Copper's malleability allows artists to create intricate designs and patterns, making it a popular choice for sculptures, jewelry, and decorative items.
Production Process and Techniques:
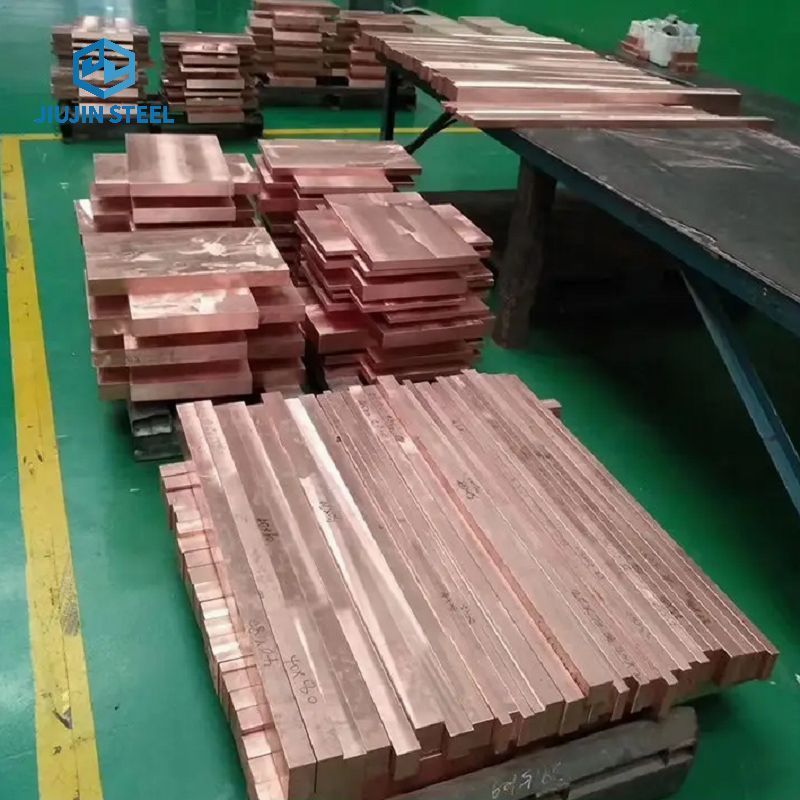
Copper plates are manufactured through a multi-step process that includes:
1. Copper Extraction: Copper ores are mined from underground or open-pit mines. The ore is then processed to extract the valuable copper metal. The extraction process can involve several stages, including crushing, grinding, and flotation, to separate the copper minerals from the ore.
2. Smelting and Purification: The extracted copper concentrate is then smelted in a furnace to produce blister copper, which contains impurities such as sulfur, iron, and other elements. The blister copper undergoes additional purification processes,such as electrolysis or fire refining, to remove these impurities and produce high-purity copper.
3. Casting and Rolling: The purified copper is cast into slabs or billets, which are then heated and hot-rolled or cold-rolled into thin sheets or strips. The rolling process reduces the thickness of the copper and improves its mechanical properties. Cold rolling produces thinner sheets with higher strength, while hot rolling allows for larger sizes and more rapid production.
4. Annealing and Finishing: After rolling, the copper plates undergo annealing, a heat treatment process that relieves internal stresses and improves the material's ductility and electrical conductivity. The plates are heated to a specific temperature and then slowly cooled. This process helps to align the copper's crystal structure and enhance its properties. The plates are then trimmed, leveled, and finished to achieve the desired surface smoothness and dimensions.