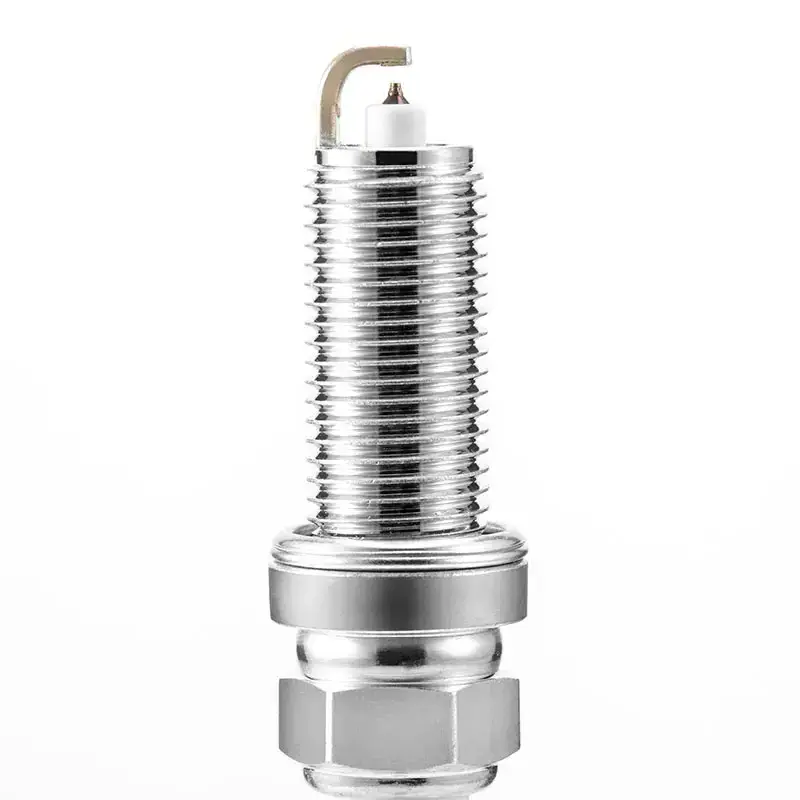
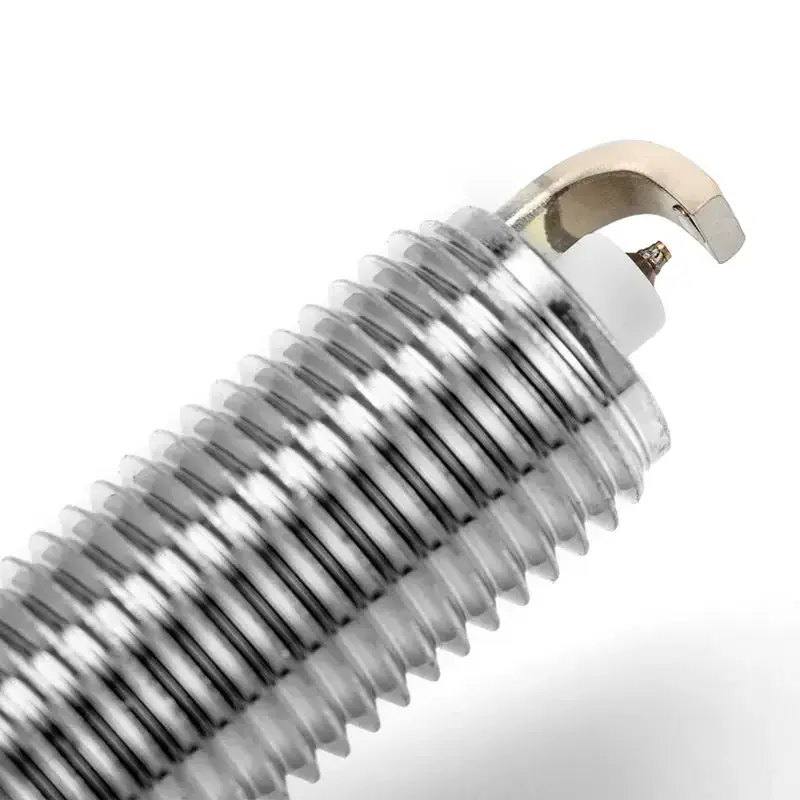
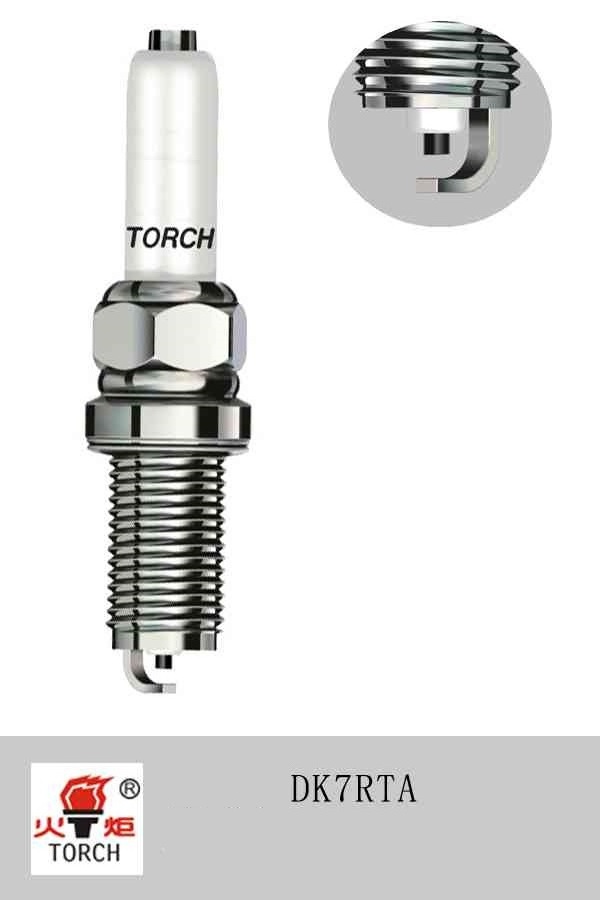
- Product Details
- {{item.text}}
Quick Details
-
Place of Origin:
-
China
-
Brand Name:
-
Torch
-
Car Model:
-
Wuling
Quick Details
-
OE NO.:
-
06H905601A
-
Thread size:
-
14
-
Warranty:
-
1 year
-
Place of Origin:
-
China
-
Brand Name:
-
Torch
-
Car Model:
-
Wuling
Product Description
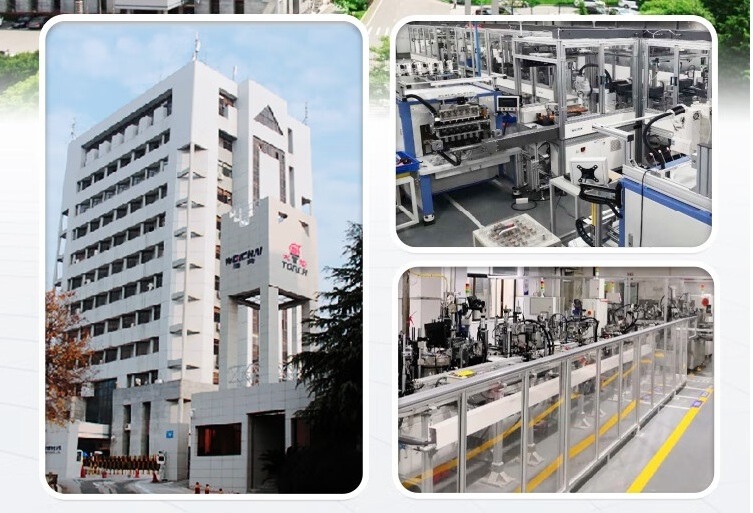



Specification
|
Certification
|
Quality Assurance
|
|
Brand
|
Torch
|
|
Material
|
Nickel alloy
|
|
OE cover
|
New Santana/Lavida/Langxing/New Passat/Jetta/Golf 7/Sagitar/Jingrui/Mingrui/Nodi
|
Packing & Delivery
To better ensure the safety of your goods, professional, environmentally friendly, convenient and efficient packaging services will be provided.10 pieces per box, packed with fillers according to the order quantity, and packaged in carton. The quantity will be determined by stacking the carton onto pallets and wrapping them with stretch film.
FAQ
What does a spark plug do?Spark plug’s basic function is to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber of a petrol engine. Spark plugs provide a path for electrical energy from the ignition coil to generate a spark needed for this air-fuel mixture. The quality of the ignition spark directly affects several factors for both the quality of the driving experience and the environment. These include starting, smooth running, general engine performance and efficiency as well as the reduction of harmful. What are the symptoms of bad spark plugs?
Symptoms of bad spark plugs include reduced fuel economy, rough idling, engine misfiring and difficulty starting the engine.
Symptoms of bad spark plugs include reduced fuel economy, rough idling, engine misfiring and difficulty starting the engine.
Why do spark plugs fail?
There are a variety of reasons why spark plugs fail. These include: old age (recommended replacement interval has been ignored), carbon build up, overheating, oil present in the combustion chamber and the incorrect spark gap.
What metal is used in spark plugs?
A variety of different metals can be used in spark plugs. Almost all spark plugs feature a copper cored inner central electrode because copper is an excellent electrical conductor. Copper, however, is a very soft metal with low resistance which means that it is not suitable as an outer center or ground electrode. Standard range of plugs feature a nickel alloy outer center electrode (fused to an inner copper core) and a nickel ground (side) electrode. The company’s premium range features extremely hard metals like iridium and platinum which guarantee longer replacement intervals.
How often do you need to change spark plugs?
This depends on a range of conditions such as the engine’s condition, if the plugs were correctly installed, the type of metal present on the plug’s outer center and ground electrodes etc. Generally, the driver or rider should refer to the maintenance intervals recommended by the manufacturer. In this context standard nickel spark plugs need to be replaced earlier than precious metal spark plug types that are more resistant with regards to wear.
Is spark plug torque necessary?
It is absolutely necessary to tighten a spark plug to the specified turning angle or torque setting. If the torque is set too low, there is a risk of compression loss. Additionally, the insulator and electrodes may also be damaged as a result of excessive vibrations. If the torque is set too high, however, the metal shell of the spark plug will be over-stressed, increasing the likelihood of it yielding or expanding. Expansion can cause the heat dissipation zones to be disrupted. Overheating, melting of the electrodes and even engine damage are other potential outcomes.
What causes carbon fouling on spark plugs?
Common reasons for this include the wrong spark plug heat range, a non-optimal engine combustion process and poor running conditions like continuous low-speed driving and short trips. A spark plug must reach a temperature of 450°C before it starts to self-clean by burning off carbon deposits. Regular short trips and continuous low-speed driving, however, result in the spark plug being unable to reach this critical temperature, making conditions for fouling ripe.
There are a variety of reasons why spark plugs fail. These include: old age (recommended replacement interval has been ignored), carbon build up, overheating, oil present in the combustion chamber and the incorrect spark gap.
What metal is used in spark plugs?
A variety of different metals can be used in spark plugs. Almost all spark plugs feature a copper cored inner central electrode because copper is an excellent electrical conductor. Copper, however, is a very soft metal with low resistance which means that it is not suitable as an outer center or ground electrode. Standard range of plugs feature a nickel alloy outer center electrode (fused to an inner copper core) and a nickel ground (side) electrode. The company’s premium range features extremely hard metals like iridium and platinum which guarantee longer replacement intervals.
How often do you need to change spark plugs?
This depends on a range of conditions such as the engine’s condition, if the plugs were correctly installed, the type of metal present on the plug’s outer center and ground electrodes etc. Generally, the driver or rider should refer to the maintenance intervals recommended by the manufacturer. In this context standard nickel spark plugs need to be replaced earlier than precious metal spark plug types that are more resistant with regards to wear.
Is spark plug torque necessary?
It is absolutely necessary to tighten a spark plug to the specified turning angle or torque setting. If the torque is set too low, there is a risk of compression loss. Additionally, the insulator and electrodes may also be damaged as a result of excessive vibrations. If the torque is set too high, however, the metal shell of the spark plug will be over-stressed, increasing the likelihood of it yielding or expanding. Expansion can cause the heat dissipation zones to be disrupted. Overheating, melting of the electrodes and even engine damage are other potential outcomes.
What causes carbon fouling on spark plugs?
Common reasons for this include the wrong spark plug heat range, a non-optimal engine combustion process and poor running conditions like continuous low-speed driving and short trips. A spark plug must reach a temperature of 450°C before it starts to self-clean by burning off carbon deposits. Regular short trips and continuous low-speed driving, however, result in the spark plug being unable to reach this critical temperature, making conditions for fouling ripe.
Hot Searches













